Category: Class 9
Average Speed And Average Velocity
Average Speed And Average Velocity In the realm of physics, both average speed and average velocity are concepts used to describe motion. Despite their similarities, they have distinct meanings and implications.

Average Speed:
Average speed is a scalar quantity that measures the overall rate at which an object covers distance during its entire journey. It is calculated by dividing the total distance traveled by the total time taken. The formula for average speed is:
Average Speed=Total Distance Total Time
Average speed provides an overview of how fast an object moves on average, without considering its direction. For instance, if a car travels 200 kilometers in 4 hours, its average speed would be 50 kilometers per hour (km/h).
Average Velocity:
Average velocity is a vector quantity that combines both the magnitude (speed) and direction of an object’s displacement over a specific time interval. It is the change in position divided by the change in time. The formula for average velocity is:
Average Velocity=Displacement Time Interval
Unlike average speed, average velocity considers the displacement of an object from its initial position to its final position. If a person moves 50 meters eastward and then returns 30 meters westward in 10 seconds, their average velocity would be 50 m−30 m10 s=2 m/s to the east.
Key Differences:
- Scalar vs. Vector: Average speed is a scalar quantity that only involves magnitude, while average velocity is a vector quantity that incorporates both magnitude and direction.
- Consideration of Direction: Average speed does not consider direction, whereas average velocity takes both direction and magnitude into account.
- Example: Imagine a car moving in a circular path. If the car returns to its starting point after some time, its average speed over that time might be significant, but its average velocity will be zero because the displacement is zero.
In conclusion, average speed characterizes the overall rate of motion without considering direction, while average velocity provides a more comprehensive picture by including both the direction and magnitude of displacement.
Both concepts are vital tools for describing and understanding the complexities of motion in physics.
Vector Nature:
The vector nature of average velocity makes it a more comprehensive representation of motion. It conveys not only how far something has traveled but also the path it took to get there. This is crucial when you’re interested in the object’s overall movement pattern.
Constant Speed vs. Changing Speed:
Average speed doesn’t differentiate between segments of motion with varying speeds. For example, if a car travels at 30 km/h for half the journey and 60 km/h for the other half, its average speed is 45 km/h (total distance divided by total time).
On the other hand, average velocity accounts for changes in speed and direction, giving you a better understanding of how the object moves overall.
In essence, while both average speed and average velocity offer insights into motion, their considerations of direction and displacement set them apart. The choice of which to use depends on the specific context and what aspects of motion you’re seeking to understand.
Read More
- Differences Between Acceleration And Velocity
- Matter In Our Surroundings Class 9 Summary
- Class 9th Chapter 2 Science Question Answer of NCERT
- NCERT Physics Class 9 Chapter 1 Solutions PDF Download
- CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 9 Science
Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
What is the difference between average speed and average velocity?
Average speed is a scalar quantity that represents the total distance traveled divided by the total time taken, without regard to direction. Average velocity is a vector quantity that accounts for both the displacement and direction of an object’s motion over a specific time interval.
Can average speed be greater than average velocity?
Yes, average speed can be greater than average velocity. This can occur when an object covers a considerable distance in a given time interval, but its overall displacement is relatively small or zero due to changes in direction.
Is the magnitude of average velocity always equal to average speed?
Not necessarily. While the magnitude of average velocity (absolute value) can be equal to average speed in cases where motion is unidirectional, it can differ when there are changes in direction during the motion.
What does a negative average velocity signify?
A negative average velocity indicates that the object has moved in the opposite direction of its initial reference point. It signifies that the displacement has occurred in the negative direction of the coordinate system.
How is average velocity calculated when the direction changes?
When the direction changes, you need to consider the total displacement, not just the total distance traveled. Calculate the difference between the initial and final positions, and then divide it by the total time taken.
Differences Between Acceleration And Velocity
Differences Between Acceleration And Velocity: Physics is a field that describes and explains the fundamental principles governing the behavior of the universe.

In the realm of mechanics, two key concepts are often discussed: acceleration and velocity. While they both relate to the motion of objects, they represent distinct aspects of an object’s movement and carry different meanings and implications.
This article aims to elucidate the differences between acceleration and velocity, highlighting their definitions, units, calculations, and real-world applications.
Differences Between Acceleration And Velocity
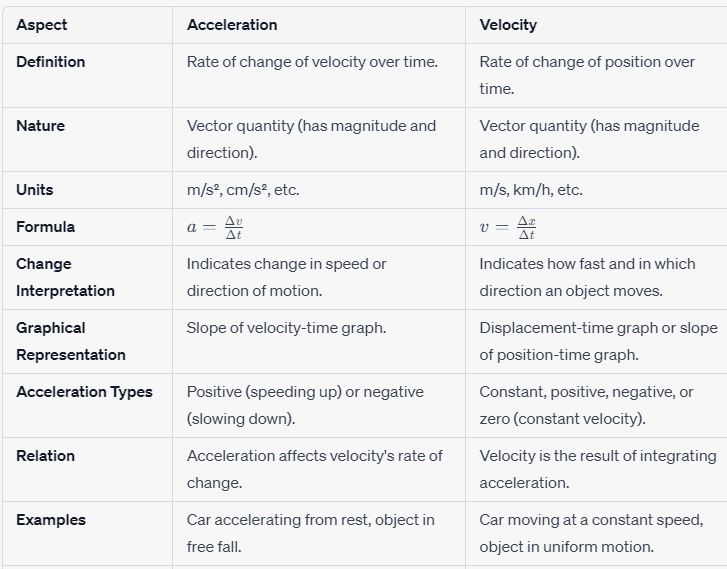
1. Definition and Nature:
Velocity refers to the rate of change of an object’s position concerning time. It is a vector quantity, which means it has both magnitude (numerical value) and direction. In simple terms, velocity informs us how fast an object is moving and in which direction it is headed.
Acceleration, on the other hand, signifies the rate of change of an object’s velocity concerning time. It is also a vector quantity, encompassing magnitude and direction. Acceleration portrays the change in an object’s speed or the alteration in its direction of motion.
2. Units:
Velocity is typically measured in units of distance divided by units of time, such as meters per second (m/s), kilometers per hour (km/h), or even feet per second (ft/s) depending on the context.
Acceleration is measured in units of change in velocity divided by units of time. Common units include meters per second squared (m/s²) and centimeters per second squared (cm/s²).
3. Calculations:
To calculate velocity, you can use the following formula:
Velocity(v) = Change in position(Δx)/Change in time(Δt)
For acceleration, the formula is:
Acceleration(a)=Change in velocity(Δv)/Change in time(Δt)
4. Relationship:
Velocity and acceleration are related in the sense that acceleration affects the change in velocity. When an object undergoes a constant acceleration, its velocity changes uniformly over time. If an object is accelerating in the same direction as its initial velocity, it speeds up. If it’s accelerating in the opposite direction, it slows down.
5. Real-World Examples:
Imagine a car accelerating from a standstill at a traffic light. Initially, the car’s velocity is zero because it’s not moving. As the car accelerates, its velocity increases in the direction of motion. This increase in velocity signifies positive acceleration.
Now, consider a car braking to come to a stop. As the driver presses the brakes, the car’s velocity decreases until it comes to a complete halt. This decrease in velocity denotes negative acceleration, often referred to as deceleration.
6. Graphical Representation:
Velocity and acceleration can be graphically represented over time. A velocity-time graph would show a slope corresponding to the acceleration. A constant slope indicates constant acceleration, while a changing slope signifies changing acceleration.
An acceleration-time graph would depict the rate of change of velocity over time. The slope of this graph represents the actual acceleration.
Newton’s Second Law of Motion
Newton’s Second Law of Motion is a fundamental principle in classical mechanics that establishes the relationship between the net force acting on an object, its mass, and the resulting acceleration. It states that the accel. of an object is directly proportional to the net force applied to it and inversely proportional to its mass. Mathematically, this law is expressed as:
Where:
- represents the net force applied to the object.
- is the mass of the object.
- signifies the resulting acceleration.
This law highlights that when an external force is applied to an object, it causes the object to accelerate in the direction of the force. Additionally, the greater the force applied, the greater the resulting acceleration, provided the mass remains constant. Conversely, if the mass increases while the force remains constant, the acceleration decreases.
Newton’s Second Law also encapsulates the concept of inertia, which is an object’s resistance to changes in its state of motion.
Objects with larger masses exhibit greater inertia, requiring more force to produce the same acceleration as objects with smaller masses.
This law provides a foundational framework for understanding and predicting the behavior of objects in motion under the influence of external forces.
Conclusion:
In the realm of physics and mechanics, the concepts of velocity and acceleration play crucial roles in describing and understanding the motion of objects.
While velocity reveals the speed and direction of an object’s movement, acceleration reveals how that velocity is changing over time.
These distinctions are vital for comprehending the complexities of motion and form the foundation for various scientific and technological advancements.
Whether you’re observing a rocket launch, calculating the motion of planets, or designing safer vehicles, a clear grasp of the differences between acce. and velocity is essential.
Read Also
- Matter In Our Surroundings Class 9 Summary
- Class 9th Chapter 2 Science Question Answer of NCERT
- NCERT Physics Class 9 Chapter 1 Solutions PDF Download
- CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 9 Science
Frequently Asked Question – FAQs on Differences Between Acceleration And Velocity
What is the fundamental difference between acceleration and velocity?
The fundamental difference lies in their definitions. Velocity is the rate of change of an object’s position concerning time and includes both speed and direction. Acceleration is the rate of change of an object’s vel. over time, indicating how much an object’s speed or direction of motion is changing.
Are velocity and acceleration scalar or vector quantities?
Both velocity and acceleration are vector quantities. This means they have both magnitude (numerical value) and direction.
How are velocity and acceleration units measured?
Velocity is measured in units of distance divided by units of time, such as meters per second (m/s) or kilometers per hour (km/h). Acceler. is measured in units of change in vel. divided by units of time, such as meters per second squared (m/s²).
Can an object have constant velocity and still be accelerating?
No, constant velocity implies that an object is moving at a steady speed in a straight line without changing direction. Acce. indicates a change in velocity, either in terms of speed or direction.
What does positive acceleration mean?
Positive acceleration occurs when an object’s vel. is increasing over time. It could mean the object is speeding up in the same direction as its initial motion or slowing down in the opposite direction.
Matter In Our Surroundings Class 9 Summary

Matter In Our Surroundings Class 9 Summary: Matter is all around us; it’s the substance that occupies space and has mass. In the realm of science, understanding matter and its various properties is crucial.
The study of matter begins with the class of substances known as “Matter in Our Surroundings.” This topic, covered in Class 9 of the CBSE curriculum (and equivalent standards), provides a fundamental understanding of the nature and behavior of matter in different states.
“Matter in Our Surroundings” is a chapter from the Class 9 Science curriculum that focuses on introducing students to the concept of matter, its various states, and the properties associated with these states. Here’s a summary of the key points covered in this chapter:
Matter In Our Surroundings Class 9 Summary
Following topics are covered in class 9 chapter 1 Matter and Surroundings
States of Matter:
-
- Introduction to the three primary states of matter: solid, liquid, and gas.
- Explanation of how the arrangement and movement of particles differ in each state.
Kinetic Theory of Matter:
-
-
- Definition and explanation of the Kinetic Theory of Matter.
- Understanding that particles are in constant motion, and their kinetic energy increases with temperature.
- Relationship between temperature and the state of matter.
-
Change of State:
- Explanation of various processes that involve changing the state of matter:
- Melting: Solid to liquid.
- Freezing: Liquid to solid.
- Evaporation: Liquid to gas.
- Condensation: Gas to liquid.
- Sublimation: Solid to gas.
- Deposition: Gas to solid.
- Description of how energy is gained or lost during these state changes.
Effect of Pressure and Temperature:
- Discussion of the influence of pressure and temperature on the states of matter.
- Explanation of how changes in pressure and temperature can lead to changes in state.
Diffusion:
- Definition and explanation of diffusion as the movement of particles from higher to lower concentration.
- Factors affecting the rate of diffusion, including temperature, particle size, and intermolecular forces.
Brownian Motion:
- Introduction to Brownian motion as the random movement of microscopic particles suspended in a fluid.
- Significance of Brownian motion in demonstrating the kinetic behavior of particles.
Importance in Daily Life:
- Illustration of the practical applications of understanding matter and its behavior in everyday situations.
- Examples of how knowledge of matter’s properties and states contributes to various fields and activities.
Matter In Our Surroundings Class 9 Summary
States of Matter:
Matter exists in three primary states: solid, liquid, and gas. These states are defined by the arrangement and movement of particles within a substance.
In solids, particles are tightly packed and have a fixed shape and volume. Liquids have particles that are close together but can move past each other, allowing them to take the shape of their container.
Gases have particles that are widely spaced and move freely, leading to indefinite shape and volume.
Kinetic Theory of Matter:
The Kinetic Theory of Matter explains the behavior of particles in different states. It posits that particles are in constant motion, with their kinetic energy increasing as temperature rises.
When heated, particles gain energy and move more vigorously, leading to changes in state. Cooling reduces particle movement, resulting in a state change as well.
Change of State:
Substances can change from one state to another through processes like melting, freezing, evaporation, condensation, sublimation, and deposition.
Melting is the transition from solid to liquid, while freezing is the reverse. Evaporation involves the conversion from liquid to gas, and condensation is the opposite process.
Sublimation occurs when a solid changes directly into a gas, bypassing the liquid state, and deposition is the reverse of sublimation.
Effect of Pressure and Temperature: Matter In Our Surroundings Class 9 Summary
Both pressure and temperature have a significant impact on the states of matter. Increasing pressure can force gases to condense into liquids and liquids to freeze into solids.
On the other hand, higher temperatures can cause solids to melt into liquids and liquids to evaporate into gases. This relationship is best described by phase diagrams, which show the conditions at which a substance exists in a specific state.
Diffusion:
Diffusion is the process of particles moving from regions of higher concentration to lower concentration until a uniform distribution is achieved.
It is a common phenomenon in gases and liquids, driven by the random motion of particles. Factors such as temperature, particle size, and intermolecular forces influence the rate of diffusion.
Brownian Motion:
Brownian motion is the erratic, random movement of microscopic particles suspended in a fluid (liquid or gas).
It was first observed by Robert Brown and serves as direct evidence of the kinetic behavior of particles in fluids.
Importance in Daily Life:
Understanding matter and its behavior has practical applications in our daily lives. From cooking to transportation, from weather changes to medical advancements, knowledge of the properties of matter and its various states helps us comprehend and manipulate the world around us.
Read Also
- Class 9th Chapter 2 Science Question Answer of NCERT
- NCERT Physics Class 9 Chapter 1 Solutions PDF Download
- CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 9 Science
- NCERT Science Book Class 9 Solutions Pdf Free Download
Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs on Matter In Our Surroundings Class 9 Summary
What is the main focus of the topic “Matter in Our Surroundings” in Class 9?
The main focus of this topic is to introduce students to the concept of matter, its various states (solid, liquid, gas), the kinetic theory explaining the behavior of particles in these states, and the processes of changing states due to factors like temperature and pressure.
What are the three primary states of matter?
The three primary states of matter are solid, liquid, and gas. These states are defined by the arrangement and movement of particles within a substance.
What does the Kinetic Theory of Matter explain?
The Kinetic Theory of Matter explains that particles in all states of matter are in constant motion. It states that as temperature increases, the kinetic energy of particles also increases, leading to changes in state.
What are the processes involved in changing the state of matter?
The processes of changing the state of matter are:
-
- Melting: Solid to liquid.
- Freezing: Liquid to solid.
- Evaporation: Liquid to gas.
- Condensation: Gas to liquid.
- Sublimation: Solid to gas.
- Deposition: Gas to solid.
How does pressure affect the states of matter?
Increasing pressure can cause gases to condense into liquids and liquids to freeze into solids. Decreasing pressure can lead to the opposite changes in state.
Class 9th Chapter 2 Science Question Answer of NCERT
Welcome to an insightful Class 9th Chapter 2 Science Question Answer of NCERT – a journey that delves into the world of scientific inquiry and understanding.
In this article, we will unravel the intricate web of questions and answers that this chapter presents, guiding you through the fundamental principles of science and encouraging a deeper comprehension of the natural phenomena that surround us.

Class 9th Science, Chapter 2, serves as a crucial stepping stone in the educational voyage, laying the foundation for a broader understanding of scientific concepts.
As we navigate through this chapter’s questions and seek their answers, we will not only enhance our knowledge but also nurture our curiosity about the way the world works.
From the tiniest atoms to the vast expanse of the cosmos, science offers us a lens through which we can view the universe. This chapter prompts us to question, to analyze, and to seek logical explanations for the various phenomena that shape our reality.
By addressing these questions and grasping the underlying principles, we open doors to discovery and innovation, empowering ourselves to make informed decisions in an increasingly complex world.
So, let us embark on this intellectual journey, where we shall engage with questions that pique our curiosity, challenge our thinking, and ultimately equip us with a deeper appreciation for the wonders of the natural world.
As we explore the Science Class 9th Chapter 2 question answers, we invite you to join us in this exploration of knowledge and insight.
Class 9th Chapter 2 Science Question Answer of NCERT
Read Also
- NCERT Physics Class 9 Chapter 1 Solutions PDF Download
- CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 9 Science
- NCERT Science Book Class 9 Solutions Pdf Free Download
- Matter In Our Surroundings Class 9 Notes Pdf Download
Class 9th Chapter 2 Science Question Answer of NCERT
Class 9th Science is a foundational step in a student’s academic journey, offering insights into the fundamental principles governing the natural world.
This subject bridges the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical applications, providing a holistic understanding of diverse scientific disciplines like physics, chemistry, and biology. Its significance lies in cultivating critical thinking skills, problem-solving abilities, and fostering a scientific temperament.
By unraveling the mysteries behind everyday phenomena, Class 9th Science empowers students to make informed decisions about their environment, health, and society.
The subject encourages curiosity-driven inquiry, equipping students with tools to question assumptions, explore hypotheses, and arrive at evidence-based conclusions.
Moreover, it prepares students to address global challenges such as climate change and technological advancements, offering the skills necessary to adapt and contribute constructively.
Beyond the classroom, Class 9th Science holds relevance in a wide array of careers, from medicine and engineering to research and technology.
This subject sparks curiosity, nurturing a lifelong passion for learning and discovery. As students delve into the intricacies of scientific principles, they lay the foundation for future academic pursuits and develop a holistic perspective on the world around them.
Introduction to Chapter 2 and its Significance
Chapter 2 of Class 9th Science embarks on a captivating journey into the heart of scientific exploration.
This chapter serves as a gateway to understanding the intricate relationships that govern the physical world, delving into fundamental concepts that underpin the natural phenomena we encounter daily.
Its significance lies in its role as a cornerstone for building a strong scientific foundation, fostering critical thinking, and inspiring curiosity.
At its core, Chapter 2 invites students to question the “how” and “why” of various scientific phenomena.
From the behavior of matter to the principles governing motion, this chapter acts as a guiding light, illuminating the path to discovery.
It introduces key concepts that form the bedrock of advanced scientific studies, making it an essential stepping stone for students aspiring to pursue diverse careers in science and technology.
The chapter’s significance extends beyond the classroom walls. By unraveling the principles behind seemingly complex phenomena, students are empowered to decipher the mysteries of the universe and make informed decisions in an ever-evolving world.
It encourages a scientific mindset that fosters critical analysis, logical reasoning, and problem-solving skills – qualities that are indispensable not only in scientific pursuits but also in various aspects of life.
Explanation Of The Fundamental Concepts Covered In The Chapter
In Class 9th Chapter 2 of Science, students are introduced to fundamental concepts that unlock the secrets of matter and its transformations.
Exploring the three states of matter – solid, liquid, and gas – this chapter delves into the microscopic world of particles, revealing how atoms and molecules interact to give rise to different forms of matter.
The chapter elucidates the processes of change of state, where matter transitions between solid, liquid, and gas due to varying temperature and pressure conditions.
It unveils the intriguing concept of latent heat, explaining the energy exchange during these changes without altering temperature. Evaporation, a common phenomenon, is dissected, along with its factors and applications.
Boiling, both as a process and its dependence on pressure, is demystified, leading to an understanding of practical applications like cooking and steam engines. Sublimation, where solids transform directly into gases, is explored, as is diffusion – the movement of particles leading to the mixing of substances.
These concepts collectively lay the groundwork for comprehending the behavior of matter and its dynamic transformations.
By grasping the molecular intricacies underlying these phenomena, students develop a foundational understanding crucial for advanced scientific studies.
The chapter not only uncovers the science behind everyday occurrences but also fosters an inquisitive mindset, nurturing a lifelong curiosity about the intricacies of the natural world.
Real-life Applications of Class 9th Chapter 2 Science Question Answer of NCERT
The concepts covered in Class 9th Chapter 2 of Science have a multitude of real-life applications that extend beyond the classroom. Here are some examples of how these concepts are relevant in everyday life:
- Cooking Processes: The understanding of states of matter and their changes is crucial in cooking. Boiling water for pasta or steaming vegetables relies on the principles of boiling and evaporation. Pressure cookers work by raising the boiling point through increased pressure, leading to faster cooking times.
- Climate Control and HVAC Systems: The principles of evaporation and condensation play a significant role in climate control systems. Air conditioning units use evaporation of refrigerants and condensation to cool indoor spaces effectively.
- Medicine and Pharmaceuticals: The concept of sublimation finds application in freeze-drying pharmaceuticals and preserving delicate substances like vaccines. It’s also used in making dry powdered medications.
- Food Preservation: Freeze-drying and sublimation are used to preserve food items like freeze-dried fruits and instant coffee. By removing moisture, these processes extend the shelf life of products.
- Transportation and Engines: Understanding the behavior of gases and pressure is essential in designing engines. Steam engines, for instance, utilize the principle of boiling to produce mechanical work.
Conclusion
Class 9th Science, as explored in this article, is not just a subject but a gateway to understanding the world in a structured and systematic manner. It equips students with the tools they need to decipher the complexities of the natural world, fostering critical thinking, problem-solving skills, and a scientific outlook. By unraveling the mysteries of everyday phenomena, students are empowered to make informed decisions that impact their environment, health, and society.
The significance of Class 9th Science extends beyond the classroom, touching various facets of life. It lays the foundation for diverse career paths, from medicine and engineering to research and technology, while also instilling a lifelong passion for learning and discovery. This subject introduces fundamental concepts that form the basis for advanced scientific studies and practical applications in various industries.
Chapter 2 serves as a pivotal milestone in this journey, offering insights into the behavior of matter and its dynamic transformations. Through understanding states of matter, change of state, evaporation, diffusion, and more, students gain a deep appreciation for the scientific principles that shape the world around them.
Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
What is the significance of Chapter 2 in Class 9th Science?
This chapter lays the groundwork for understanding the behavior of matter and its changes. It introduces fundamental concepts like states of matter, change of state, evaporation, and diffusion, forming the basis for more advanced scientific studies.
Why is understanding the states of matter important?
States of matter (solid, liquid, gas) are fundamental to our everyday experiences. Understanding their properties and transitions helps explain a wide range of phenomena, from boiling water to the behavior of gases.
How does evaporation differ from boiling?
Evaporation occurs at the surface of a liquid, even at temperatures below its boiling point. While boiling is a bulk process involving the entire liquid and happens at its boiling point.
What is latent heat, and why is it important?
Latent heat is the heat energy absorbed or released during a change of state without temperature change. It’s crucial as it explains why temperature remains constant during processes like melting and boiling.
How does diffusion work, and why is it significant?
Diffusion is the mixing of particles due to their random motion. It’s important for understanding processes like the spread of odors, the mixing of substances, and even cellular processes in biology.
NCERT Physics Class 9 Chapter 1 Solutions PDF Download

The NCERT Physics Class 9 Chapter 1 Solutions serve as an instant and effective way for students to resolve any uncertainties they may have.
These solutions serve as a guiding light, leading students through the essential concepts outlined in the CBSE Class 9 Science curriculum. By engaging with the exercises provided in the textbook, students can establish a solid grasp of the subject matter.
In the process of tackling these exercises, students often encounter questions that give rise to uncertainties. This is precisely where the NCERT Solutions for Class 9 prove invaluable. They furnish concise explanations and comprehensive answers to address these uncertainties.
Encompassing pivotal chapters such as Matter, Atoms, Tissues, Living Organisms, Motion, Force, Laws of Motion, Gravitation, Energy and Work, Sound, Natural Resources, among others, these CBSE Science NCERT Solutions for Class 9 comprehensively cover the gamut of important topics contained within the textbook.
NCERT Physics Class 9 Chapter 1 Solutions PDF Download
Read Also
- Matter In Our Surroundings Class 9 Sample Paper With Answers
- Class 9 Science Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings Notes
- NCERT Science Book Class 9 Solutions Pdf Free Download
- Matter In Our Surroundings Class 9 Notes Pdf Download
- Important Questions of Matter in Our Surroundings Class 9
- Class 9th Chapter 2 Science Question Answer of NCERT
NCERT Physics Class 9 Chapter 1 Solutions PDF Download
When it comes to fostering a solid foundation in the realm of physics, NCERT (National Council of Educational Research and Training) resources have stood the test of time as a beacon of clarity and understanding.
The NCERT Physics Class 9 Chapter 1 Solutions, available for download in PDF format, serve as an invaluable tool for students embarking on their scientific journey. In this article, we delve into the significance of these solutions and explore how they contribute to a deeper understanding of the subject matter.
Chapter 1: Matter in Our Surrounding
The journey through the Class 9 science textbook embarks with a captivating exploration of “Matter in Our Surroundings.” The very fabric of the world around us consists of a substance known as matter.
These tangible entities occupy space and possess mass, forming the building blocks of our reality. In ancient times, Indian philosophers discerned five fundamental elements that constituted matter, referred to as Panch Tatva – encompassing air, water, earth, sky, and fire.
However, the paradigm has shifted with the advent of modern science, unveiling dual classifications rooted in physical properties and chemical behaviors. This opening chapter takes students on a voyage into the realm of matter’s physical attributes.
Matter, though imperceptibly minute, is composed of particles. These elemental constituents maintain infinitesimal gaps between them, incessantly in motion, while simultaneously exerting an attractive force upon each other.
Our immediate surroundings harbor matter in three distinct states: solid, liquid, and gas. These states emerge from the nuanced traits exhibited by the constituent particles.
Delving into a rich tapestry of activities, this chapter unravels the intricacies of all three states, elucidating their essence.
Crucially, the text unfurls the notion that the state of matter is not fixed but mutable. A metamorphosis between states is achievable by manipulating temperature or pressure.
The phenomenon of a liquid’s transformation into vapor beneath its boiling point is labeled as evaporation. Factors influencing the rate of evaporation span the surface area exposed to the environment, ambient temperature, humidity levels, and wind velocity.
Notably, evaporation wields a cooling effect, an intriguing facet that adds depth to our comprehension of matter’s behavior.
The Importance of NCERT Physics Class 9 Chapter 1 Solutions
Chapter 1 of NCERT’s Physics textbook for Class 9 is a crucial stepping stone, introducing students to the fundamental concepts that underpin the world of physics.
From measurements and units to the meticulous process of measurement, this chapter lays the groundwork for future scientific exploration. However, navigating these concepts can sometimes prove challenging, and that’s where the NCERT Physics Class 9 Chapter 1 Solutions come into play.
Aiding Clarity Through Comprehensive Solutions
The downloadable PDF solutions act as a supportive companion, addressing the various exercises and questions posed in the textbook.
Each solution is meticulously crafted to offer a clear, step-by-step elucidation of the problem-solving process. This clarity not only helps students arrive at the correct answers but also equips them with a deep understanding of the underlying principles.
Benefits of PDF Format
The availability of NCERT Physics Class 9 Chapter 1 Solutions in PDF format further enhances their accessibility. Students can conveniently download the solutions onto their devices, allowing for easy reference and study even when offline.
This digital approach aligns perfectly with the modern education landscape, where technology plays a pivotal role in learning.
Promoting Self-Directed Learning
One of the hallmarks of effective learning is the ability to think critically and independently. The NCERT Physics Class 9 Chapter 1 Solutions facilitate this by offering not just answers, but explanations that encourage students to grasp the concepts and apply them to different scenarios. This fosters self-directed learning, an essential skill that goes beyond the classroom.
Preparation for Assessments
As students progress through their academic journey, assessments become an integral part of the learning process. The NCERT Physics Class 9 Chapter 1 Solutions play a significant role in aiding preparation for tests and exams. By practicing with these solutions, students can familiarize themselves with various question formats and fine-tune their problem-solving abilities.
Inclusivity and Accessibility
One of the key tenets of NCERT resources is their commitment to inclusivity and accessibility. The availability of free PDF downloads for the Physics Class 9 Chapter 1 Solutions aligns with this ethos, ensuring that quality education is within reach for students from all walks of life.
Conclusion
In a world where knowledge is just a few clicks away, the NCERT Physics Class 9 Chapter 1 Solutions PDF download exemplifies the marriage of traditional education principles with modern technology.
These solutions not only facilitate learning but also empower students to take charge of their academic growth. As students venture into the fascinating world of physics, these solutions stand as a reliable companion, illuminating the path to a deeper understanding of the subject.
Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs on NCERT Physics Class 9 Chapter 1 Solutions
Q1: What is the significance of the chapter “Matter in Our Surroundings” in Class 9 Science?
The chapter “Matter in Our Surroundings” serves as the foundation for understanding the basic concepts of matter and its properties. It introduces students to the various states of matter and explains how they can change from one state to another.
Q2: What is matter, and how is it classified according to modern science?
Matter refers to anything that occupies space and has mass. According to modern science, matter can be classified based on physical properties and chemical nature. This classification helps in understanding the diverse characteristics of different materials.
Q3: How did ancient Indian philosophers classify matter?
Ancient Indian philosophers classified matter into five basic elements known as “Panch Tatva.” These elements are air, water, earth, sky, and fire. This classification was rooted in philosophical and cultural beliefs.
Q4: What are the three states of matter discussed in the NCERT Physics Class 9 Chapter 1 Solutions?
The chapter discusses three states of matter: solid, liquid, and gas. These states are determined by the arrangement and movement of particles that constitute matter.
Q5: How do particles of matter behave in different states?
In solids, particles are densely arranged and maintain a fixed structure. However, in liquids, particles are more loosely organized and have the ability to flow past one another. In gases, particles are widely dispersed and exhibit unrestricted movement.
CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 9 Science

Access CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 9 Science: This comprehensive study resource, tailored for Class 9 Science students, serves as an invaluable tool for thorough exam preparation.
CBSE releases the previous year’s question papers and their solutions shortly after the exams conclude, offering students valuable insight.
Furthermore, CBSE supplies an exam marking scheme and blueprint for the forthcoming test. By reviewing previous year’s questions and their solutions, students can assess their performance and enhance their skills for future endeavors.
The most effective method for progress is consistent revision – engage extensively with past year question papers. If you’re in search of CBSE’s Class 9 Science previous year question papers with solutions, they are available for download here.
CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 9 Science
Read Also
- CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 9 Maths with Solutions
- Sample Question Paper for Class 9 CBSE Hindi Course B
- Matter In Our Surroundings Class 9 Sample Paper With Answers
- Class 9 Science Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings Notes
- Class 9th Chapter 2 Science Question Answer of NCERT
CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 9 Science
You know, when it comes to doing well in school, it’s like a game plan, right? And one super important tool in this game is those CBSE Previous Year Question Papers for Class 9 Science.
They’re not just regular old papers – they’re like your secret map to success! No matter how things change in school, these papers stay super valuable.
They help you really understand the subject and get you all set for the big exam showdown. So, let’s dive in and see why these papers are like your ultimate sidekick for doing awesome in Class 9 Science!
Significance of CBSE Class 9 Science Previous Year Papers
CBSE Class 9 Science Previous Year Papers hold remarkable significance in a student’s academic journey. They serve as a crucial bridge between classroom learning and real exam performance.
These papers are more than just practice tests; they offer valuable insights into the exam format, question trends, and topic weightage. By revisiting these papers, students gain a clear understanding of the subjects and concepts that are likely to be tested.
These papers provide a sneak peek into the actual exam environment, helping students acclimate to the pressure and structure of the test.
Moreover, they offer not only questions but also answers, enabling students to identify their strengths and areas for improvement. This personalized feedback is akin to having a mentor guide them through the learning process.
In a dynamic educational landscape, where curriculum and teaching methods may change, core concepts remain constant.
Previous Year Papers enable students to identify these enduring concepts and allocate their study efforts effectively. By reviewing these papers, students can fine-tune their preparation strategies, enhance time management skills, and boost their confidence.
Ultimately, CBSE Class 9 Science Previous Year Papers serve as a compass, directing students toward a successful exam performance. They offer a road map of what to expect, provide a means to track progress, and instill the confidence needed to tackle the real exam with vigor and assurance.
Importance of Previous Year Question Papers
Previous Year Question Papers hold a pivotal role in a student’s academic journey, offering multifaceted advantages that contribute significantly to their preparation and success. These papers are far more than mere artifacts of the past; they are valuable tools with several key benefits.
Firstly, these papers provide a window into the exam’s structure and pattern. By analyzing the types of questions, distribution of marks, and overall format, students can familiarize themselves with the blueprint of the upcoming exam. This familiarity reduces anxiety and enhances confidence, as students approach the test day with a clear understanding of what to expect.
Secondly, Previous Year Question Papers offer insights into question trends and topic importance. These trends help students identify recurring themes and concepts that are likely to be tested again. Consequently, students can prioritize their revision efforts, focusing on the core areas that carry a higher probability of appearing in the exam.
Thirdly, these papers serve as effective tools for self-assessment and improvement. By attempting questions from previous years, students can gauge their strengths and weaknesses. The accompanying solutions allow them to pinpoint areas where they made errors and learn from those mistakes. This iterative process fosters a deeper understanding of the subject matter.
How to Make the Most of Previous Year Papers
To extract the utmost value from Previous Year Papers, adopt a strategic approach that transcends mere repetition.
Regular practice should be fused into your study routine, encompassing diverse questions from various years to foster familiarity with different question styles and topics.
Unveiling patterns and trends across multiple years’ papers helps you pinpoint recurring themes and question types, prioritizing study efforts on topics more likely to appear in the upcoming exam.
However, it’s essential not to stop at surface-level solutions; a profound understanding of underlying concepts is pivotal. Simulating exam conditions by setting time limits while practicing sharpens time management skills.
Embrace errors as avenues for learning, scrutinizing incorrect answers to grasp their reasons and rectify knowledge gaps. Encourage a dynamic learning cycle by revisiting textbooks to reinforce understanding of challenging questions.
Incorporate a mix of papers from diverse years to expose yourself to various question patterns and trends. Utilize note-taking to compile key insights, formulas, and strategies. If hurdles persist, don’t hesitate to seek guidance from teachers or peers.
For heightened preparedness, engage in mock exams, simulating full-length tests under exam conditions. In essence, the objective is to foster a deep comprehension of concepts and nurture problem-solving skills.
Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
1. What are CBSE Previous Year Question Papers for Class 9 Science?
These are question papers from past years’ CBSE Class 9 Science exams. They provide actual exam-like questions and are a valuable resource for practice and preparation.
2. Why should I use CBSE Previous Year Question Papers?
These papers offer insights into exam patterns, question trends, and important topics. They help you become familiar with the exam format and boost your confidence.
3. Are CBSE Previous Year Question Papers still relevant even if the syllabus changes?
Yes, they are still relevant. While the syllabus might see minor changes, core concepts remain consistent. These papers help you understand the type of questions that can appear and how to approach them.
4. How can CBSE Previous Year Question Papers help in improving my performance?
By practicing these papers, you can assess your strengths and weaknesses, learn from mistakes, manage time better, and gain clarity on important topics. This leads to improved performance.
5. Where can I find CBSE Previous Year Question Papers for Class 9 Science?
You can find these papers on various educational websites, online forums, and even the CBSE official website. They are often available for free download.
NCERT Science Book Class 9 Solutions Pdf Free Download

NCERT Science Book Class 9 Solutions Pdf Free Download: The NCERT Science Book for Class 9 is an invaluable educational tool that lays the foundation for a comprehensive understanding of scientific concepts.
To assist students in mastering the subject, NCERT Science Book Class 9 Solutions are now readily available in PDF format for free download.
This article delves into the importance of these solutions and provides insights into how to access them.
NCERT Science Book Class 9 Solutions Pdf Free Download
- Chapter 1: Matter in Our Surroundings
- Chapter 2: Is Matter Around Us Pure
- Chapter 3: Atoms and Molecules
- Chapter 4: Structure of the Atom
- Chapter 5: Fundamental Unit of Life
- Chapter 6: Tissues
- Chapter 7: Diversity in Living Organisms
- Chapter 8: Motion
- Chapter 9: Force and Laws of Motion
- Chapter 10: Gravitation
- Chapter 11: Work and Energy
- Chapter 12: Sound
- Chapter 13: Why Do We Fall Ill
- Chapter 14: Natural Resources
- Chapter 15: Improvement in Food Resources
Read Also
- Matter In Our Surroundings Class 9 Notes Pdf Download
- Important Questions of Matter in Our Surroundings Class 9
- Matter In Our Surroundings Class 9 Sample Paper With Answers
- Class 9 Science Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings Notes
- MCQ for Class 9 Science Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings
- Class 9th Chapter 2 Science Question Answer of NCERT
NCERT Science Book Class 9 Solutions Pdf Free Download
Importance of NCERT Science Book Class 9 Solutions
- Aiding Conceptual Grasp: The NCERT Science Book for Class 9 covers a diverse range of topics that lay the groundwork for advanced studies. However, students often grapple with comprehending complex theories and principles. NCERT Science Book Class 9 Solutions act as illuminating guides, breaking down intricate ideas into manageable fragments.
- Elevating Problem-Solving Acumen: Science isn’t just about theories—it’s about applying knowledge to real-world scenarios. These solutions present students with a variety of problems and guide them through the step-by-step process of arriving at solutions. This nurtures their analytical thinking and equips them with invaluable problem-solving skills.
- Navigating Textbook Exercises: Textbook exercises are pivotal in reinforcing what students learn in class. NCERT Science Book Class 9 Solutions function as companions, providing clear, concise explanations to exercises that might otherwise prove challenging.
Understanding the Significance of NCERT Science Book Class 9 Solutions
The National Council of Educational Research and Training (NCERT) is renowned for producing high-quality textbooks that align with the curriculum prescribed by various educational boards in India.
The NCERT Science Book for Class 9 serves as a pivotal resource for students to grasp fundamental scientific principles across various topics such as matter, energy, organisms, and more.
While the textbook itself is comprehensive, students often encounter challenges while solving exercises and understanding complex concepts.
This is where NCERT Science Book Class 9 Solutions come to the rescue. These solutions provide step-by-step explanations to the textbook exercises, enabling students to grasp the underlying concepts and problem-solving techniques.
They bridge the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical application, helping students enhance their analytical skills and achieve academic excellence.
Advantages of Accessing NCERT Science Book Class 9 Solutions PDF
- Comprehensive Understanding: The solutions offer detailed explanations to a wide range of questions, ensuring that students understand the subject matter thoroughly.
- Problem-Solving Skills: By following the solutions, students learn effective problem-solving strategies that can be applied to different scenarios, fostering a deeper understanding of the subject.
- Self-Paced Learning: Students can learn at their own pace, using the solutions as a reference to clarify doubts and reinforce their understanding.
- Exam Preparation: As the solutions cover a variety of question types, students gain a competitive advantage in exams by practicing with similar problems.
- Concept Clarification: Complex concepts are broken down into simple steps, making it easier for students to grasp and retain information.
How to Access NCERT Science Book Class 9 Solutions PDF for Free
You can download all chapter’s solutions from the above given links. This is the quickest way of pdf download. Although there are various way to access pdf online.
- Official NCERT Website: The most reliable source for NCERT solutions is the official NCERT website (www.ncert.nic.in). Navigate to the “E-Books” section and locate the solutions for the Class 9 Science Book.
- Educational Platforms: Numerous educational websites and platforms host free NCERT solutions. Simply search for “NCERT Class 9 Science Book Solutions PDF” on search engines to find these resources.
- Mobile Apps: There are several mobile applications available on app stores that offer NCERT solutions for various subjects. Download a trusted app and explore the Class 9 Science solutions.
- Online Education Portals: Many online education portals provide free access to NCERT solutions. These platforms are user-friendly and make it easy to navigate through the solutions.
Conclusion
The NCERT Science Book Class 9 Solutions PDFs offer a valuable lifeline to students aiming to excel in science.
By providing comprehensive explanations and problem-solving strategies, these solutions empower students to tackle challenges with confidence.
Accessing these solutions for free ensures that quality education is within the reach of every student, supporting their academic journey and fostering a love for learning.
Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
Q1: What are NCERT Science Book Class 9 Solutions?
NCERT Science Book Class 9 Solutions are step-by-step explanations and answers to the exercises and questions found in the NCERT Science textbook for Class 9. These solutions help students understand concepts better and improve their problem-solving skills.
Q2: Why are NCERT Science Book Class 9 Solutions important?
These solutions play a crucial role in enhancing students’ understanding of complex scientific concepts. They provide clarity on textbook exercises, helping students master the subject and prepare effectively for exams.
Q3: Where can I find NCERT Science Book Class 9 Solutions PDF for free?
You can access NCERT Science Book Class 9 Solutions PDF for free from sources like the official NCERT website (www.ncert.nic.in), educational websites, mobile apps, and online education portals. Searching for “NCERT Class 9 Science Book Solutions PDF” online will yield various options.
Q4: How can NCERT Science Book Class 9 Solutions PDF benefit exam preparation?
The solutions cover a variety of question types, allowing students to practice extensively and build confidence for exams. By understanding the problem-solving techniques, students can effectively tackle similar questions in their exams.
Q5: Are NCERT Science Book Class 9 Solutions suitable for self-paced learning?
Yes, these solutions are designed to facilitate self-paced learning. Students can refer to the solutions to clarify doubts, reinforce concepts, and study at their own convenience.
Matter In Our Surroundings Class 9 Notes Pdf Download
Matter In Our Surroundings Class 9 Notes Pdf Download: Understanding the properties and behavior of matter is a fundamental aspect of science. Matter forms the building blocks of everything around us, from the air we breathe to the food we eat and the objects we interact with daily.
In Class 9, students delve into the intriguing world of matter in their science curriculum. This article provides an overview of the key concepts covered in the “Matter in Our Surroundings” chapter, offering a glimpse into the diverse forms and properties of matter.
Matter In Our Surroundings Class 9 Notes Pdf Download

Download PDF of Matter In Our Surroundings Class 9 Notes
Matter In Our Surroundings Class 9 Notes Pdf Download
Introduction to Matter:
Matter is anything that occupies space and has mass. It can exist in three main states: solid, liquid, and gas. These states are determined by the arrangement and motion of particles that make up the matter.
States of Matter:
- Solid: In the solid state, particles are closely packed and have a fixed shape and volume. They vibrate in place, but their positions remain relatively constant. Examples of solids include wood, metal, and ice.
- Liquid: In the liquid state, particles are still close together, but they can move past one another, allowing liquids to flow and take the shape of their container. Liquids have a definite volume but not a fixed shape. Water, milk, and oil are common examples of liquids.
- Gas: Gaseous particles have significant separation between them and move rapidly in all directions. They do not have a fixed shape or volume, as they take the shape of their container and can expand to fill it completely. Examples of gases include air, oxygen, and carbon dioxide.
Kinetic Theory of Matter:
The kinetic theory of matter helps explain the behavior of particles in different states. It states that particles in matter are in constant motion due to their kinetic energy.
The temperature of a substance is directly related to the average kinetic energy of its particles. As a substance is heated, its particles gain energy and move more vigorously.
Change of State:
Matter can change from one state to another through processes such as melting, freezing, evaporation, condensation, sublimation, and deposition.
- Melting: The process of changing a solid into a liquid due to the absorption of heat.
- Freezing: The process of changing a liquid into a solid due to the release of heat.
- Evaporation: The process of changing a liquid into a gas at temperatures below its boiling point.
- Condensation: The process of changing a gas into a liquid due to cooling.
- Sublimation: The direct conversion of a solid into a gas without passing through the liquid state.
- Deposition: The direct conversion of a gas into a solid without passing through the liquid state.
Measurement of Matter:
Matter is measured in terms of its mass and volume. Mass is the amount of matter in an object, while volume is the amount of space it occupies. The standard unit of mass is the kilogram (kg), and the standard unit of volume is the cubic meter (m³).
Diffusion:
Diffusion is the process by which particles of a substance spread out and mix with the particles of another substance due to their random motion. This phenomenon is often observed when substances like perfume, smoke, or gases spread and mix in the air.
Conclusion of Matter In Our Surroundings Class 9 Notes Pdf Download
The study of matter in our surroundings provides valuable insights into the physical properties and behaviors of different substances.
From the simple concepts of states of matter to the complex processes of change and diffusion, Class 9 students gain a foundational understanding of the matter that forms the basis of our world.
As they continue their educational journey, this knowledge serves as a stepping stone to more advanced scientific principles and applications.
Read Also:
- Important Questions of Matter in Our Surroundings Class 9
- MCQ for Class 9 Science Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings
- Matter In Our Surroundings Class 9 Sample Paper With Answers
- CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 9 Maths with Solutions
- Sample Question Paper for Class 9 CBSE Hindi Course B
- Class 9th Chapter 2 Science Question Answer of NCERT
Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs on Matter In Our Surroundings Class 9 Notes Pdf Download
1. What is the “Matter in Our Surroundings” chapter about?
The “Matter in Our Surroundings” chapter in Class 9 science deals with the fundamental concepts of matter, its states, properties, and behavior in different conditions.
2. Why is it important to study matter?
Studying matter helps us understand the physical world around us, from everyday substances to complex scientific phenomena. It forms the foundation for various scientific disciplines.
3. What are the three main states of matter discussed in the chapter?
The chapter discusses three states of matter: solid, liquid, and gas. These states are determined by the arrangement and movement of particles in matter.
4. How do particles behave in the solid state?
In the solid state, particles are tightly packed and have a fixed shape and volume. They vibrate in place due to thermal energy.
5. How is the kinetic theory of matter relevant to this chapter?
The kinetic theory of matter explains how particles in matter are in constant motion due to their kinetic energy. It helps us understand properties and changes in different states of matter.
Important Questions of Matter in Our Surroundings Class 9
Important Questions of Matter in Our Surroundings Class 9: In the world of science, there’s a really important topic we’re going to talk about: stuff around us, like things we see and touch. In Class 9, we start digging into this cool stuff – tiny pieces, different things, and how they all work together. Everything around us, you know, is made of tiny bits called matter. And guess what? Matter has its own set of mysteries that we’re here to solve!

As we get into it, we find ourselves asking all sorts of questions. How do those super tiny pieces behave? Why do some things change shape or size? What’s up with everyday things like water, air, and even the smell of your favorite food? These are the kind of questions we’re going to tackle in this article. We want to help you understand the neat things about matter and give you a peek into how scientists explore all these cool ideas.
Important Questions of Matter in Our Surroundings Class 9 (Short Answer)
Q 1: Describe the process of chromatography. What is it used for?
Chromatography is a technique used to separate and analyze components of a mixture based on their different affinities for a stationary phase (e.g., paper) and a mobile phase (e.g., solvent). As the mobile phase moves through the stationary phase, different components of the mixture move at different rates, allowing for separation. It is used for analyzing the composition of substances, such as in forensics or chemical research.
Q 2: Why do we see water droplets on the outer surface of a glass containing ice-cold water?
This phenomenon is called condensation. When warm, humid air comes into contact with a cold surface (such as the glass of ice-cold water), the air cools down. As a result, its ability to hold moisture decreases, causing the water vapor in the air to condense into tiny water droplets on the cold surface.
Q 3: How does the pressure exerted by a gas change with an increase in temperature?
According to Gay-Lussac’s law, at constant volume, the pressure exerted by a gas is directly proportional to its absolute temperature (measured in Kelvin). As the temperature of a gas increases, its pressure also increases, assuming the volume remains constant.
Q 4: Explain the concept of diffusion. Provide examples from everyday life.
Diffusion is the spontaneous mixing of particles of different substances due to their random motion. Examples include the scent of perfume spreading in a room, the dispersion of ink in water, or the aroma of cooking food spreading throughout a house.
Q 5: What is the effect of altitude on boiling point and cooking time?
As altitude (elevation above sea level) increases, atmospheric pressure decreases. Since boiling point is the temperature at which vapor pressure equals atmospheric pressure, the lower atmospheric pressure at high altitudes results in a lower boiling point. This affects cooking times because foods may cook at lower temperatures, requiring longer cooking times due to the reduced heat transfer efficiency.
Important Questions of Matter in Our Surroundings Class 9 (Long Answer)
Q 1: Define matter. Give examples of different states of matter.
Matter is anything that has mass and occupies space. It’s what makes up the physical substances around us. Everything you can touch, see, smell, or interact with is made up of matter. Matter is composed of tiny particles called atoms and molecules.
There are three main states of matter: solid, liquid, and gas. Let’s look at some examples of each:
Solid: Solids have a definite shape and volume. The particles in a solid are closely packed and arranged in a regular pattern. They vibrate in place, but their positions don’t change much. Examples of solids include:
- Ice: Water frozen into a solid state.
- Wood: The material that forms the trunks and branches of trees.
- Iron: A metal that’s often used to make tools and structures
Liquid: Liquids have a definite volume but no fixed shape. The particles in a liquid are still close together, but they are not as tightly packed as in solids. They can move past each other, allowing liquids to flow and take the shape of their container. Examples of liquids include:
- Water: Essential for life, it’s the most common liquid on Earth.
- Milk: A white liquid produced by mammals as food for their young.
- Juice: A flavorful liquid extracted from fruits.
Gas: Gases have neither a definite shape nor a fixed volume. The particles in a gas are spread far apart and move rapidly, filling any available space. Gases can be compressed or expanded easily. Examples of gases include:
-
- Oxygen: A gas vital for respiration, found in the air we breathe.
- Helium: A gas lighter than air, often used to fill balloons.
- Carbon Dioxide: A gas produced by animals and used by plants during photosynthesis.
Q 2: Explain the characteristics of the three states of matter: solid, liquid, and gas.
Certainly! Let’s delve into the characteristics of the three states of matter: solid, liquid, and gas.
1. Solid:
- Definite Shape: Solids have a fixed shape. The particles in a solid are tightly packed and arranged in a regular, repeating pattern, which gives the solid its distinct shape.
- Definite Volume: Solids also have a definite volume, meaning they occupy a specific amount of space.
- Particle Arrangement: The particles in a solid are closely bonded to each other. They vibrate in place but generally do not move from their positions.
2. Liquid:
- No Definite Shape: Liquids take the shape of their container. They do not have a fixed shape of their own.
- Definite Volume: Similar to solids, liquids also have a definite volume, meaning they occupy a specific amount of space.
- Particle Movement: The particles in a liquid are still close together, but they have more freedom to move past each other. This allows liquids to flow and take the shape of their container.
3. Gas:
- No Definite Shape or Volume: Gases have neither a fixed shape nor a definite volume. They expand to fill the entire space available to them.
- Particle Movement: The particles in a gas are widely spaced and move rapidly in all directions. They have high kinetic energy, leading to constant movement.
- Weak Intermolecular Forces: The forces between gas particles are very weak. This allows gases to diffuse quickly and spread out.
Q 3: Differentiate between evaporation and boiling.
Evaporation and boiling are both processes by which a liquid turns into a vapor or gas, but they occur under different conditions and have distinct characteristics. Here’s how they differ:
Evaporation:
- Definition: Evaporation is the process by which a liquid changes into a vapor or gas at temperatures below its boiling point. It occurs at the surface of the liquid.
- Temperature: Evaporation occurs at various temperatures, even at room temperature. It does not require the liquid to reach its boiling point.
- Speed: Evaporation is a relatively slow process. Only the particles with higher energy escape from the liquid’s surface, leading to a gradual vaporization.
- Bubbles: Unlike boiling, evaporation does not produce bubbles in the liquid.
- Example: When water left in an open container slowly disappears over time, it’s undergoing evaporation.
Boiling:
- Definition: Boiling is the process by which a liquid changes into a vapor or gas rapidly and uniformly throughout the liquid, usually at its boiling point.
- Temperature: Boiling occurs at a specific temperature called the boiling point. It’s the point at which the vapor pressure of the liquid equals the atmospheric pressure.
- Speed: Boiling is a much faster process compared to evaporation. It involves the formation of bubbles within the liquid, which rise to the surface and release vapor.
- Bubbles: Boiling is characterized by the formation of bubbles within the liquid. These bubbles are filled with vapor and rise to the surface, where they burst and release vapor into the air.
- Example: When you heat water in a kettle on a stove, the bubbles you see forming and rising are a result of boiling.
Q 4: Explain the process of sublimation with examples.
Sublimation is a unique phase transition in which a substance changes directly from a solid to a gas without passing through the liquid state. This occurs when the vapor pressure of the solid becomes greater than the atmospheric pressure at a specific temperature. Sublimation is the reverse of deposition, where a gas changes directly into a solid without becoming a liquid first. This process is fascinating and not as common as melting, boiling, or evaporation.
Here’s how sublimation works, along with some examples:
Process of Sublimation:
- Solid to Gas: In sublimation, a solid substance gains enough energy from its surroundings to break its intermolecular bonds and transition into a gas without becoming a liquid first.
- Temperature and Pressure: Sublimation typically occurs at temperatures and pressures where the substance’s vapor pressure exceeds the atmospheric pressure. This can vary for different substances.
Examples of Sublimation:
- Dry Ice (Solid Carbon Dioxide): Dry ice is a well-known example of sublimation. It’s a solid form of carbon dioxide (CO2) that changes directly into carbon dioxide gas without melting into a liquid. Dry ice is often used in fog machines for special effects or in shipping to keep items cold without wetting them.
- Camphor: Camphor, a white solid with a distinct odor, sublimes when exposed to air. This is why camphor stored in an open container eventually disappears, leaving no liquid residue behind.
- Mothballs: Mothballs are made of substances like naphthalene or paradichlorobenzene, which readily sublime. They transition from solid to gas over time, releasing the vapor that helps repel insects.
Q 5: Discuss the factors affecting the rate of evaporation.
The rate of evaporation, which is the process of a liquid turning into a vapor or gas, is influenced by several factors. Understanding these factors can help explain why some liquids evaporate faster than others and how the process can be manipulated. Here are the main factors that affect the rate of evaporation:
1. Temperature: Higher temperatures generally lead to faster evaporation. When the temperature is higher, the particles in the liquid gain more kinetic energy, which means they move faster. This increased energy allows more particles to break free from the liquid’s surface and become vapor.
2. Surface Area: A larger surface area exposed to the air increases the rate of evaporation. More molecules are near the surface and can escape into the air. This is why a shallow container of water will evaporate faster than the same amount of water in a deeper container.
3. Air Movement (Wind): Air movement, often caused by wind, enhances evaporation. Moving air carries away the moisture-saturated air near the surface of the liquid, allowing fresh, drier air to take its place. This maintains a higher concentration gradient and encourages more rapid evaporation.
4. Humidity: Humidity is the amount of water vapor present in the air. High humidity levels mean that the air is already holding a significant amount of moisture, reducing the rate of evaporation. Lower humidity levels create a larger difference in water concentration between the liquid and the air, leading to faster evaporation.
5. Vapor Pressure: Vapor pressure is the pressure exerted by the vapor of a substance in equilibrium with its liquid phase at a specific temperature. Higher vapor pressure means more particles are escaping from the liquid into the air, which increases the rate of evaporation.
Q 6: Why do gases exert pressure on their containers?
Gases exert pressure on their containers due to the constant and random motion of their particles, which collide with the walls of the container. This phenomenon is described by the kinetic theory of gases and is rooted in the principles of molecular motion and collisions.
Here’s how it works:
- Particle Motion: Gas particles (atoms or molecules) are in continuous, rapid motion. They move in straight lines until they collide with other particles or the walls of the container.
- Collisions with Container Walls: When gas particles collide with the walls of the container, they exert a force on the wall. These collisions create pressure by transferring momentum to the container’s surface.
- Magnitude of Pressure: The pressure exerted by a gas is a result of the cumulative effect of countless particle collisions over the entire inner surface of the container. The pressure depends on the frequency and force of these collisions.
- Uniform Distribution: The collisions occur uniformly in all directions because the gas particles move randomly in all three dimensions. This leads to an equal distribution of pressure on all inner surfaces of the container.
- Ideal Gas Law: The behavior of gases is described by the ideal gas law (PV = nRT), where P represents pressure, V is volume, n is the number of moles of gas, R is the ideal gas constant, and T is temperature. This law provides a mathematical relationship between pressure, volume, and other gas properties.
Read Also:
- MCQ for Class 9 Science Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings
- Matter In Our Surroundings Class 9 Sample Paper With Answers
- Class 9 Science Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings Notes
- CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 9 Maths with Solutions
- Sample Question Paper for Class 9 CBSE Hindi Course B
Importance of Questions of Matter in Our Surroundings Class 9
Studying the questions about stuff around us is super important in Class 9 science. It helps us understand what things are made of and why they do certain things. We learn about solid, liquid, and gas – how they change and act. This helps us with everyday things like cooking, drying, and even environmental problems. Knowing this basic stuff gets us ready for more complex science later.
It’s like a puzzle piece that fits into bigger scientific ideas. Learning about particles – those tiny building blocks of everything – gets our brains curious and thinking. We start asking questions, which is how science grows. This helps us solve problems and make smart choices.
Plus, this knowledge isn’t just for school. It’s for real life too. Think about how ice melts or how food cooks – it’s all about matter and how it behaves. Understanding this can even lead to cool jobs in medicine, making things, and lots more. So, studying these matter questions isn’t just about school – it’s about getting ready for a world full of interesting stuff and exciting possibilities.
Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
Q 1: What affects the rate of evaporation?
Factors like temperature, surface area, humidity, air movement (wind), and the nature of the liquid can influence how fast a liquid evaporates.
Q 2: Why is understanding matter important?
Understanding matter is crucial because everything around us is made of it. It helps us explain how things work, from cooking to drying clothes, and even how gases behave in our environment.
Q 3: How can we see sublimation in everyday life?
You can see sublimation when dry ice (solid carbon dioxide) turns into a smoky gas without melting, or when mothballs disappear over time.
MCQ for Class 9 Science Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings
Presented below are the MCQ for Class 9 Science Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings from Chemistry. These multiple-choice questions are aligned with the CBSE board curriculum and are designed to match the latest syllabus for Class 9 chemistry.
By engaging with these MCQs, students can efficiently recapitulate the concepts discussed in the chapter, aiding them in their preparation for the Class 9 Annual examinations, as well as for other entrance exams like CTET and KVS.

MCQ for Class 9 Science Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings
1: Which of the following is not a physical change?
a) Melting of ice
b) Burning of paper
c) Evaporation of water
d) Dissolution of salt in water
2: The process of changing a substance from solid to liquid is called:
a) Condensation
b) Sublimation
c) Melting
d) Evaporation
3: The boiling point of water at standard atmospheric pressure is:
a) 0°C
b) 100°C
c) 273 K
d) 373 K
4: In which state of matter do particles have the highest kinetic energy?
a) Solid
b) Liquid
c) Gas
d) Plasma
5: Which of the following is a characteristic property of gases?
a) Definite shape
b) Definite volume
c) High compressibility
d) Strong intermolecular forces
6: The process of conversion of a liquid into its vapor below its boiling point is called:
a) Evaporation
b) Boiling
c) Sublimation
d) Condensation
7: Which of the following substances sublimes directly from solid to gas?
a) Iodine
b) Sodium chloride
c) Sugar
d) Copper
8: The phenomenon in which a solid directly changes into gas without passing through the liquid state is called:
a) Melting
b) Sublimation
c) Evaporation
d) Condensation
9: The SI unit of temperature is:
a) Celsius
b) Kelvin
c) Fahrenheit
d) Rankine
10: The process of converting a gas into a liquid is called:
a) Vaporization
b) Evaporation
c) Condensation
d) Sublimation
11: The intermolecular forces in solids are generally:
a) Very weak
b) Stronger than in liquids
c) Absent
d) Equal to the forces in gases
12: Which of the following substances has the highest rate of evaporation at room temperature?
a) Water
b) Mercury
c) Oil
d) Salt
13: The temperature at which a solid starts melting is called its:
a) Boiling point
b) Melting point
c) Freezing point
d) Sublimation point
14: The process of changing a substance from a gas directly to a solid is called:
a) Condensation
b) Sublimation
c) Vaporization
d) Melting
15: Which state of matter has the highest intermolecular forces and the least kinetic energy?
a) Solid
b) Liquid
c) Gas
d) Plasma
16: The process of conversion of a liquid into its vapor at any temperature is called:
a) Evaporation
b) Boiling
c) Sublimation
d) Condensation
17: Which of the following does not affect the rate of evaporation?
a) Surface area of the liquid
b) Temperature of the liquid
c) Humidity of the air
d) Atmospheric pressure
18: The process of conversion of a gas directly into a solid is known as:
a) Condensation
b) Sublimation
c) Vaporization
d) Melting
19: The density of an object decreases when it is:
a) Heated
b) Cooled
c) Compressed
d) Sublimated
20: The process of changing a liquid into a solid is called:
a) Condensation
b) Vaporization
c) Freezing
d) Melting
21: The kinetic energy of particles is highest in which state of matter?
a) Solid
b) Liquid
c) Gas
d) Plasma
22: Which of the following is a physical change?
a) Rusting of iron
b) Digestion of food
c) Burning of wood
d) Evaporation of water
23: The boiling point of a liquid is dependent on:
a) The volume of the liquid
b) The color of the liquid
c) The type of container
d) The atmospheric pressure
24: The process of conversion of a solid directly into a gas is known as:
a) Condensation
b) Sublimation
c) Vaporization
d) Freezing
25: Which of the following is an example of sublimation?
a) Ice melting to form water
b) Water evaporating to form steam
c) Iodine crystals disappearing over time
d) Wax melting to form liquid wax
26: The process of a gas changing directly into a solid is called:
a) Condensation
b) Sublimation
c) Deposition
d) Evaporation
27: Which of the following is a chemical change?
a) Boiling of water
b) Dissolving sugar in water
c) Burning of a candle
d) Melting of butter
28: Which of the following temperature scales has no negative temperatures?
a) Celsius
b) Fahrenheit
c) Kelvin
d) Rankine
29: Which of the following statements about gases is true?
a) Gases have fixed shapes
b) Gases have fixed volumes
c) Gases are highly compressible
d) Gases have strong intermolecular forces
30: The process of changing a gas into a liquid is called:
a) Sublimation
b) Condensation
c) Evaporation
d) Melting
Answers Corresponding to the MCQ for Class 9 Science Chapter 1:
- b) Burning of paper
- c) Melting
- b) 100°C
- c) Gas
- c) High compressibility
- a) Evaporation
- a) Iodine
- b) Sublimation
- b) Kelvin
- c) Condensation
- b) Stronger than in liquids
- a) Water
- b) Melting point
- b) Sublimation
- a) Solid
- a) Evaporation
- c) Humidity of the air
- b) Sublimation
- a) Heated
- c) Freezing
- c) Gas
- d) Evaporation of water
- d) The atmospheric pressure
- b) Sublimation
- c) Iodine crystals disappearing over time
- c) Deposition
- c) Burning of a candle
- c) Kelvin
- c) Gases are highly compressible
- b) Condensation
Read Also
- Matter In Our Surroundings Class 9 Sample Paper With Answers
- Class 9 Science Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings Notes
- CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 9 Maths with Solutions
- Sample Question Paper for Class 9 CBSE Hindi Course B
MCQ for Class 9 Science Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings
“Matter in Our Surroundings” marks the first step in the captivating world of chemistry for Class 9 students. This chapter unveils the secrets of the states of matter, changes in state, and the kinetic theory of matter. As students embark on this journey, MCQs serve as their companions, offering insights and challenges along the way.
1. Comprehensive Grasp: MCQs span the breadth of the chapter, ensuring that students engage with every facet of the subject matter. From the classification of matter to the properties of solids, liquids, and gases, MCQs encourage a holistic understanding of the concepts.
2. Conceptual Clarity: Each MCQ is a portal to deeper comprehension. The process of reading the question, analyzing options, and selecting the correct answer requires a solid grasp of the underlying concepts. This goes beyond surface-level memorization and nurtures true understanding.
3. Critical Thinking Development: MCQs serve as catalysts for critical thinking. They prompt students to evaluate options, consider exceptions, and employ logical reasoning to arrive at the correct answer. This cultivates analytical skills vital for scientific exploration.
4. Immediate Feedback and Learning: The real-time feedback MCQs provide is invaluable. Students swiftly ascertain whether their answer is correct, allowing them to address misconceptions promptly. This iterative process of trial, error, and correction forms a strong foundation for learning.
5. Exam Preparedness: In the run-up to examinations, MCQ practice is a boon. Familiarity with the question format, diverse concepts covered, and the ability to manage time effectively become essential tools for success in both internal and competitive assessments.
6. Tailored Learning Experience: MCQs are adaptable to various learning styles. They can incorporate visuals, diagrams, and practical examples, catering to diverse learners and making the learning journey more engaging and inclusive.
7. Engagement and Exploration: Engaging MCQs can spark students’ curiosity and drive further exploration. Thought-provoking questions can lead to classroom discussions, independent research, and a deeper appreciation of the topic’s real-world applications.
8. Long-term Retention: The repetition of concepts via MCQ practice reinforces memory. As students revisit topics through different questions, the concepts become ingrained, ensuring long-term retention and application.
Navigating the Path with MCQs
With the advent of digital resources, students now have access to platforms offering an array of MCQs tailored to Class 9 Science Chapter 1. These platforms create a dynamic learning environment, enabling students to track their progress, identify areas of improvement, and customize their learning experience.
As students embark on the journey of “Matter in Our Surroundings,” MCQs emerge as the guiding light, illuminating the path to scientific understanding. They facilitate the transformation of learning from a routine exercise into an exciting expedition of exploration and enlightenment. In the realm of science education, MCQs are not just questions; they are the keys to unlocking the doors of knowledge and curiosity.
Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
What are MCQs in the context of Class 9 Science Chapter 1?
MCQs, or Multiple-Choice Questions, are a type of assessment format where a question is presented along with several possible answers, of which one is correct. Students are required to select the most accurate answer from the provided options.
Why are MCQs important for learning Chapter 1 “Matter in Our Surroundings”?
MCQs help students comprehensively review the key concepts covered in Chapter 1. They encourage critical thinking, conceptual clarity, and engagement with the material, making the learning process more effective and enjoyable.
How do MCQs enhance understanding of Chapter 1 concepts?
By analyzing MCQ options, students need to recall and apply their knowledge, fostering a deeper understanding of the subject matter. The process of selecting the correct answer involves reasoning, which solidifies comprehension.
How can MCQs aid in critical thinking development?
MCQs require students to evaluate multiple options and make informed choices. This process sharpens analytical skills, encourages logical reasoning, and nurtures a scientific temperament.
Can MCQs prepare students for exams and assessments?
Absolutely. MCQs provide familiarity with the question format often seen in exams. Practicing a variety of MCQs helps students prepare for internal assessments, annual exams, and competitive tests.