Difference Between Equinox And Solstice
Difference Between Equinox And Solstice: Equinox and solstice are astronomical events that mark significant points in the Earth’s orbit around the Sun, bringing about changes in seasons and daylight hours. Here’s a comparison of the key differences between equinox and solstice:
Difference Between Equinox And Solstice
1. Definition:
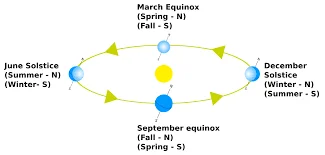
- Equinox: An equinox occurs when the Sun is directly above the Earth’s equator, resulting in nearly equal lengths of day and night. There are two equinoxes each year: the vernal equinox (spring equinox) and the autumnal equinox (fall equinox).
- Solstice: A solstice is an astronomical event when the Sun reaches its highest or lowest point in the sky at noon, marking the longest day (summer solstice) or shortest day (winter solstice) of the year.
2. Occurrence:
- Equinox: Equinoxes occur twice a year, around March 20-21 (vernal equinox) and September 22-23 (autumnal equinox) in the Northern Hemisphere. In the Southern Hemisphere, the dates are reversed.
- Solstice: Solstices also occur twice a year, around June 20-21 (summer solstice) and December 21-22 (winter solstice) in the Northern Hemisphere. In the Southern Hemisphere, the dates are reversed.
3. Daylight Hours:
- Equinox: During equinoxes, day and night are approximately of equal length in most parts of the world. This balance of daylight and darkness is often referred to as “equilux.”
- Solstice: Solstices mark the extremes of daylight hours. The summer solstice has the longest day and shortest night, while the winter solstice has the shortest day and longest night.
4. Sun’s Position:
- Equinox: In an equinox, the Sun is situated precisely above the Earth’s equator, resulting in the Sun rising directly in the east and setting directly in the west, regardless of the observer’s geographical location on Earth.
- Solstice: During a solstice, the Sun is at its highest (summer solstice) or lowest (winter solstice) point in the sky at noon, resulting in the longest or shortest noontime shadows, respectively.
5. Seasonal Significance:
- Equinox: Equinoxes signal the beginning of spring (vernal equinox) or fall (autumnal equinox) and are associated with the transition between the seasons.
- Solstice: Solstices mark the official start of summer (summer solstice) or winter (winter solstice) and represent the peak of the respective seasons.
6. Cultural and Celebratory Traditions:
- Equinox: Equinoxes have been celebrated in various cultures and religions as times of balance and renewal. For example, the vernal equinox is associated with Easter in Christianity.
- Solstice: Solstices have often been associated with major cultural and religious celebrations. For instance, the summer solstice is celebrated in festivals like Midsummer’s Eve in some cultures.
In summary, equinoxes and solstices are astronomical events that influence the length of day and night, the Sun’s position in the sky, and the changing of seasons. Equinoxes represent balance, while solstices represent extremes in daylight and are culturally significant in various parts of the world.
Read More
- Molecular Weight Of K2Cr2O7
- Molecular Weight Of Phosphorus
- Molecular Weight Of SO2
- Molecular Weight of Na2CO3
- Molecular Mass Of Sodium
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) On Difference Between Equinox And Solstice
1. What is the main difference between an equinox and a solstice?
The key difference lies in their astronomical significance. Equinoxes mark the times when day and night are nearly of equal length, signaling the transition between seasons, while solstices mark the moments when the Sun reaches its highest or lowest point in the sky, resulting in the longest or shortest day of the year.
2. How many equinoxes and solstices occur each year?
There are two equinoxes each year: the vernal (spring) equinox and the autumnal (fall) equinox. Likewise, there are two solstices: the summer solstice and the winter solstice.
3. When do equinoxes occur?
Equinoxes typically occur around March 20-21 (vernal equinox) and September 22-23 (autumnal equinox) in the Northern Hemisphere. The dates are reversed in the Southern Hemisphere.
4. When do solstices occur?
Solstices generally occur around June 20-21 (summer solstice) and December 21-22 (winter solstice) in the Northern Hemisphere, with reversed dates in the Southern Hemisphere.
5. How do equinoxes affect daylight hours?
Equinoxes bring nearly equal lengths of day and night, resulting in a balance of daylight and darkness.
