Periodic Table Class 11
Periodic Table Class 11: The periodic table is one of the foundational pillars of chemistry, and for Class 11 students embarking on their chemistry journey, it is a crucial topic to understand.
This comprehensive guide aims to provide Class 11 students with an in-depth exploration of the periodic table, covering its history, organization, periodic trends, and the significance of this iconic arrangement of elements.
Periodic Table Class 11
1. The Historical Journey of the Periodic Table
1.1 The Early Days of Chemistry:
- The study of elements and their properties dates back to ancient times, with philosophers like Aristotle contemplating the nature of substances.
- Alchemists in the Middle Ages contributed to the understanding of materials, although their methods were often mystical.
1.2 Mendeleev’s Periodic Table:
- Dmitri Mendeleev, a Russian chemist, is credited with creating the first periodic table in 1869.
- Mendeleev organized elements based on their atomic mass, noticing that elements with similar properties occurred at regular intervals.
- He left gaps for undiscovered elements and accurately predicted their properties.
1.3 The Modern Periodic Table:
- The modern periodic table is organized by increasing atomic number, which is the number of protons in an atom’s nucleus.
- Elements are arranged into periods (horizontal rows) and groups (vertical columns).
- The periodic table accommodates all known elements, including synthetic ones.
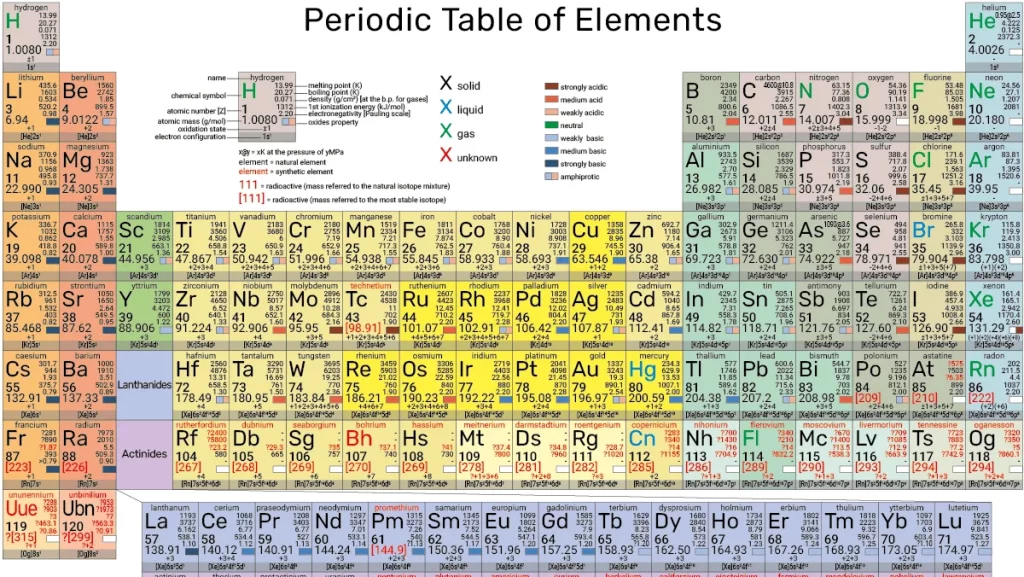 Periodic Table
Periodic Table
2.1 Periods and Groups:
- A period is a horizontal row on the periodic table, and there are seven periods in total.
- A group (or family) is a vertical column, and there are 18 groups.
- Elements in the same group share similar chemical properties due to their similar electron configurations.
2.2 Atomic Number and Atomic Mass:
- The atomic number of an element is its unique identifier, representing the number of protons in its nucleus.
- The atomic mass (or atomic weight) is the average mass of an element’s isotopes.
2.3 Electronic Configuration:
- The arrangement of electrons in an atom’s energy levels determines its chemical behavior.
- Understanding electronic configurations helps predict how elements will bond and react.
3. Elements and Their Properties
3.1 Metals, Non-Metals, and Metalloids:
- The periodic table can be divided into three main categories: metals, non-metals, and metalloids.
- Metals are typically shiny, conductive, and have high melting and boiling points.
- Non-metals are often dull, poor conductors, and have lower melting and boiling points.
- Metalloids exhibit properties of both metals and non-metals.
3.2 Representative and Transition Elements:
- Representative elements are found in the “s” and “p” blocks of the periodic table.
- Transition elements are located in the “d” and “f” blocks and are known for their variable oxidation states and colorful compounds.
4. Periodic Trends
4.1 Atomic Radius:
- Atomic radius is the size of an atom and decreases across a period and increases down a group.
- This trend is due to the effective nuclear charge and the number of electron energy levels.
4.2 Ionization Energy:
- Ionization energy is the energy required to remove an electron from an atom.
- It increases across a period and decreases down a group due to electron shielding and effective nuclear charge.
4.3 Electronegativity:
- Electronegativity is an element’s ability to attract electrons in a chemical bond.
- It increases across a period and decreases down a group.
4.4 Electron Affinity:
- Electron affinity is the energy change when an atom gains an electron.
- It generally increases across a period and decreases down a group.
5. The Significance of the Periodic Table
5.1 Predicting Element Properties:
- The periodic table allows scientists to predict the properties of elements, even those not yet discovered.
- It provides insights into an element’s reactivity, bonding behavior, and physical characteristics.
5.2 Understanding Chemical Bonding:
- The arrangement of elements in the periodic table explains how chemical bonds form.
- Elements in the same group often share similar bonding tendencies.
5.3 Analyzing Chemical Reactions:
- The periodic table helps chemists understand and predict the outcomes of chemical reactions.
- It guides reaction stoichiometry and the formation of products.
5.4 Applications in Real Life:
- The periodic table has practical applications in various fields, from materials science and medicine to environmental science and energy production.
- It is essential for designing new materials and understanding their properties.
6. Key Concepts and Practical Tips for Class 11 Students
As you study the periodic table in your Class 11 chemistry curriculum, here are some key concepts and practical tips to help you grasp this fundamental topic effectively:
6.1 Understand Periods and Groups:
- Pay close attention to the structure of the periodic table, with its rows (periods) and columns (groups).
- Recognize that elements in the same group have similar properties due to their electron configurations.
6.2 Atomic Number vs. Atomic Mass:
- Differentiate between the atomic number (Z) and atomic mass (A) of elements.
- The atomic number defines the element, while the atomic mass accounts for isotopes.
6.3 Electronic Configurations:
- Learn how to write electronic configurations for elements, as they play a crucial role in understanding reactivity and bonding.
6.4 Periodic Trends:
- Master the periodic trends of atomic radius, ionization energy, electronegativity, and electron affinity.
- Recognize how these trends change across periods and down groups.
6.5 Chemical Bonding:
- Understand how elements’ positions in the periodic table influence the type of chemical bonds they form.
- This knowledge is vital for predicting bond types and reactions.
6.6 Practice Problem-Solving:
- Solve a variety of problems related to the periodic table to reinforce your understanding.
- Work on exercises that involve predicting element behavior and calculating trends.
6.7 Real-World Applications:
- Explore the practical applications of the periodic table in various fields.
- Consider how elements are used in everyday life, technology, and industry.
7. Resources for Further Learning
To deepen your understanding of the periodic table, consider using additional resources:
- Textbooks: Consult your Class 11 chemistry textbook for in-depth explanations and practice problems related to the periodic table.
- Online Tutorials: Explore online chemistry tutorials and video lessons that provide visual explanations and demonstrations.
- Interactive Periodic Tables: Use interactive periodic tables available online or through chemistry apps. These tools allow you to explore element properties and trends interactively.
- Periodic Table Games: Engage in educational games and quizzes that make learning about the periodic table fun and interactive.
- Chemistry Forums: Join online chemistry forums or communities where you can ask questions, share knowledge, and learn from fellow students and experts.
- Laboratory Experiments: If possible, participate in chemistry laboratory experiments that involve elements from the periodic table. Hands-on experience can enhance your understanding.
8. Study Strategies for Success
To excel in your Class 11 chemistry studies, particularly when delving into the periodic table, consider the following study strategies:
8.1 Consistent Practice:
- Regularly review and practice the concepts related to the periodic table. Consistency is key to mastering this fundamental topic.
8.2 Flashcards:
- Create flashcards with element names, symbols, atomic numbers, and key properties. Use these flashcards for quick and effective revision.
8.3 Group Study:
- Collaborate with classmates for group study sessions. Discussing and teaching each other can reinforce your understanding.
8.4 Mnemonics:
- Use mnemonics or memory aids to remember the order of elements in a group or other important periodic table information.
8.5 Visual Aids:
- Utilize visual aids, such as color-coded periodic tables and diagrams, to help you grasp the organization and trends effectively.
8.6 Online Resources:
- Explore online resources, including educational websites, interactive periodic tables, and YouTube tutorials that offer alternative explanations and examples.
8.7 Regular Review:
- Periodically revisit previously learned concepts to ensure retention. This can be particularly useful for mastering periodic trends.
9. Realizing the Beauty of Chemistry
While the periodic table may seem like a static chart of elements, it holds the key to understanding the dynamic world of chemistry. As you progress through your Class 11 chemistry course, you’ll come to appreciate how this elegant arrangement of elements simplifies complex chemical phenomena.
Moreover, the periodic table transcends classroom boundaries; it’s a universal language understood by scientists worldwide. It’s a testament to human ingenuity and the power of collaboration among scientists over centuries.
Remember, the periodic table is not merely a chart—it’s a gateway to exploring the mysteries of matter, the wonders of chemical reactions, and the boundless possibilities of science. Embrace your journey into the world of chemistry, and let the periodic table be your guide.
Your curiosity and dedication will unlock a realm of knowledge that will not only enrich your academic pursuits but also deepen your appreciation for the beauty of the natural world. Happy studying!
10. Classroom and Beyond
As you progress through your Class 11 chemistry curriculum and explore the periodic table, keep in mind that chemistry extends far beyond the classroom. Here are some ways to engage with chemistry in your everyday life:
10.1 Observing the Elements:
- Look around you and identify elements in your environment. Consider the metals used in your electronics, the gases in the air you breathe, and the compounds in household items.
10.2 Chemistry in Nature:
- Explore the chemistry of the natural world. Learn about the chemical processes that occur in plants, animals, and geological formations.
10.3 Chemistry in Technology:
- Investigate how chemistry drives technological advancements. Discover how elements and compounds are used in cutting-edge innovations.
10.4 Chemistry in Medicine:
- Delve into the role of chemistry in healthcare. Learn about pharmaceuticals, medical diagnostics, and the chemistry behind disease prevention and treatment.
10.5 Environmental Chemistry:
- Explore the impact of human activities on the environment and the role of chemistry in addressing environmental challenges.
10.6 Chemistry in Art and Culture:
- Appreciate the connection between chemistry and art, from pigments used in paintings to the chemistry of cuisine.
12. Seek Guidance and Stay Curious
Remember that chemistry, including the pd table, can be a challenging subject at times, but it’s also incredibly rewarding. Don’t hesitate to seek guidance from your teachers, classmates, or online resources when you encounter difficulties. Chemistry is a subject that rewards curiosity and perseverance.
Stay curious and inquisitive. Ask questions, conduct experiments if possible, and explore chemistry-related topics that pique your interest. The pd table is just the beginning of a fascinating journey into the world of chemistry, where countless discoveries await.
As you continue your studies in Class 11 and beyond, keep in mind that chemistry is not confined to textbooks and classrooms. It’s a vibrant field that impacts every aspect of our lives. Whether you aspire to be a scientist, engineer, healthcare professional, or simply a curious learner, chemistry will provide you with valuable insights and a deeper understanding of the world around you.
Embrace the pd table as your roadmap, and let your curiosity drive your exploration of the captivating realm of chemistry. With dedication and a thirst for knowledge, you’ll find that chemistry opens doors to endless possibilities and a lifelong appreciation for the wonders of the natural world. Enjoy your journey into the world of chemistry!
The pd table is a foundational concept in chemistry that serves as a roadmap to the world of elements and their properties. As a Class 11 student, your journey through chemistry will be greatly enriched by a solid grasp of the pd table and its associated principles. Embrace the pd table as a tool that will empower you to unravel the mysteries of matter, and enjoy the adventure of discovery as you explore the fascinating world of chemistry.
Conclusion
The pd table is a foundational concept in chemistry that serves as a roadmap to the world of elements and their properties. As a Class 11 student, your journey through chemistry will be greatly enriched by a solid grasp of the pd table and its associated principles. Embrace the pd table as a tool that will empower you to unravel the mysteries of matter, and enjoy the adventure of discovery as you explore the fascinating world of chemistry.
Read More
- Molecular Weight Of Sodium Carbonate
- Difference Between Isothermal And Adiabatic Process
- Simple Harmonic Motion Examples
- Molecular Mass Of Calcium
- Molecular Weight of Chlorine
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) Periodic Table
1. What is the periodic table?
The pd table is a tabular arrangement of chemical elements, organized by their atomic number, which represents the number of protons in an atom’s nucleus. It groups elements with similar properties in columns called groups or families.
2. Who developed the first periodic table, and when was it created?
The first pd table was developed by Dmitri Mendeleev, a Russian chemist, in 1869. He organized elements based on their atomic masses and predicted the properties of undiscovered elements.
3. How are elements arranged in the periodic table?
Elements are arranged by increasing atomic number from left to right and top to bottom. They are grouped into periods (rows) and groups (columns) based on similar electronic configurations and properties.
4. What are periods and groups in the periodic table?
Periods are the horizontal rows in the pd table, numbered from 1 to 7. Groups, also known as families, are the vertical columns, numbered from 1 to 18.
5. What are representative elements and transition elements?
Representative elements, also called main group elements, are found in the “s” and “p” blocks of the pd table. Transition elements are located in the “d” and “f” blocks.
