Tag: between ac and dc generator
Difference Between Ac And Dc Generator
Difference Between Ac And Dc Generator: Generators play a vital role in our modern world by providing electrical power in various applications, from residential homes to industrial complexes.
Two common types of generators are AC (alternating current) generators and DC (direct current) generators. While their primary purpose is the same — to produce electricity — they operate on different principles and have distinct advantages and disadvantages. In this article, we will delve into the differences between AC and DC generators to help you better understand how they work and where they are used.

Difference Between Ac And Dc Generator
AC Generators
1. Operation Principle:
- AC generators, also known as alternators, operate on the principle of electromagnetic induction. When a coil of wire is rotated within a magnetic field, it induces an alternating current (AC) in the coil.
2. Output Type:
- AC generators produce alternating current, which periodically changes direction. The voltage and current values alternate between positive and negative values.
3. Voltage Regulation:
- AC generators can be designed to produce a relatively stable output voltage. Voltage regulation is achieved by adjusting the magnetic field strength or controlling the rotational speed of the generator.
4. Applications:
- AC generators are widely used for electricity generation in power plants, homes, and commercial buildings.
- They are preferred for long-distance power transmission because transformers can easily change the voltage of AC electricity, reducing losses during transmission.
DC Generators
1. Operation Principle:
- DC generators, also known as dynamos, operate on the principle of Faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction. They use a commutator and brushes to convert mechanical energy into direct current (DC).
2. Output Type:
- DC generators produce a constant, unidirectional flow of current. The voltage remains constant in polarity and magnitude.
3. Voltage Regulation:
- DC generators are known for providing a relatively stable output voltage, especially when used in conjunction with voltage regulators.
4. Applications:
- DC generators are less common in modern applications compared to AC generators.
- They were historically used in early electrical systems, such as street lighting, but have largely been replaced by AC generators.
Key Differences
1. Type of Current:
- The most fundamental difference is the type of current they produce. AC generators generate alternating current, while DC generators produce direct current.
2. Voltage Regulation:
- AC generators can be easily designed for voltage regulation, making them suitable for most power generation and distribution applications.
- DC generators also offer good voltage regulation but have become less prevalent due to the advantages of AC power distribution.
3. Use Cases:
- AC generators are the primary choice for electricity generation and distribution in the modern world.
- DC generators have limited applications today and are mainly found in specialized industries and historical installations.
4. Advantages of AC Generators:
- Versatility: AC generators can produce various voltages and frequencies to match specific requirements, making them suitable for a wide range of applications.
- Easy Transformation: AC voltage can be easily transformed using transformers, allowing for efficient long-distance power transmission.
- Availability: AC power is readily available from the electrical grid in most regions, simplifying the integration of AC generators into existing infrastructure.
5. Disadvantages of AC Generators:
- Complexity: AC generators often involve more complex control systems to regulate voltage and frequency.
- Limited DC Output: Generating direct current (DC) from an AC generator requires additional components, such as rectifiers.
6. Advantages of DC Generators:
- Constant Voltage: DC generators provide a constant voltage output, which can be advantageous for certain applications, such as battery charging.
- No Frequency Variation: DC generators do not have frequency variations like AC generators.
7. Disadvantages of DC Generators:
- Limited Applications: DC generators have a more limited range of applications in modern times due to the widespread use of AC power.
- Efficiency: AC generators are generally more efficient in large-scale power generation and distribution systems.
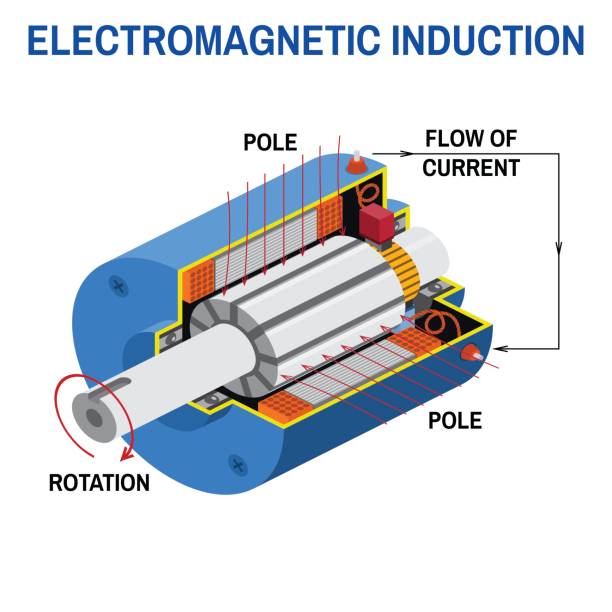

Modern electrical systems overwhelmingly favor AC power generation and distribution due to its efficiency, ease of transformation, and widespread adoption. However, DC generators still find use in specialized applications where a constant voltage or unidirectional current is required, such as in battery charging systems and certain industrial processes.
It’s important to note that advancements in power electronics and semiconductor technology have allowed for the efficient conversion of AC to DC and vice versa. This has further blurred the lines between AC and DC applications, as many devices now utilize both types of current through rectifiers and inverters.
Conclusion
AC generators and DC generators have distinct operating principles and applications. While AC generators are the backbone of modern electrical systems, DC generators continue to serve specific niches. The choice between AC and DC power generation depends on the specific needs of the application and the advantages each system offers. As technology continues to evolve, the boundaries between these two systems may continue to blur, resulting in more flexible and efficient power generation and distribution solutions.
Read More
- Excretory System Class 10
- Sodium Carbonate Molar Mass
- Layers Of The Earth
- Environmental Pollution And Recycle
- Batteries In Series Parallel
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) On Difference Between Ac And Dc Generator
1. What is the fundamental difference between AC and DC generators?
The primary difference lies in the type of current they produce. AC generators generate alternating current that periodically changes direction, while DC generators produce direct current with a constant flow in one direction.
2. How do AC generators work?
AC generators operate on the principle of electromagnetic induction. When a coil of wire rotates within a magnetic field, it induces an alternating current (AC) in the coil.
3. How do DC generators work?
DC generators, or dynamos, work based on Faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction. They use a commutator and brushes to convert mechanical energy into direct current (DC).
4. Which type of generator is more commonly used today?
AC generators are more commonly used in modern applications, especially for power generation and distribution, due to their efficiency and ease of voltage regulation.
5. What are the advantages of AC generators?
- AC generators are versatile, as they can produce various voltages and frequencies to match specific needs.
- They allow for efficient long-distance power transmission through transformers.
- AC power is readily available from the electrical grid in most regions.
Difference Between Alternator And Generator
Difference Between Alternator And Generator: Alternators and generators are both devices that convert mechanical energy into electrical energy, but they operate on different principles and have distinct characteristics. Here’s a comparison of the key differences between alternators and generators:
Difference Between Alternator And Generator
1. Operating Principle:
- Alternator: An alternator generates electricity using the principle of electromagnetic induction. It produces alternating current (AC), where the direction of current flow continuously reverses at a specific frequency.
- Generator: A generator, often referred to as a dynamo or DC generator, produces direct current (DC) through electromagnetic induction. It typically uses a commutator to convert alternating voltage into direct current.
2. Type of Current Produced:
- Alternator: Produces alternating current (AC), which periodically changes direction. The voltage and current alternate in polarity and direction.
- Generator: Produces direct current (DC), where the voltage and current flow consistently in one direction.
3. Output Voltage:
- Alternator: Alternators usually produce higher voltages (AC) suitable for many electrical applications. Voltage regulation is typically easier in alternators.
- Generator: Generators typically produce lower voltages (DC) and require additional components like voltage regulators to achieve stable output.
4. Maintenance:
- Alternator: Alternators generally require less maintenance compared to generators. They have fewer moving parts and do not have brushes and commutators, which wear out over time.
- Generator: Generators may require more maintenance due to the brushes and commutators that need periodic replacement. This maintenance can be more demanding and costly.
5. Efficiency:
- Alternator: Alternators are generally more efficient in converting mechanical energy into electrical energy. They are commonly used in modern vehicles due to their efficiency.
- Generator: Generators may have lower efficiency due to the energy losses associated with the commutator and the conversion of AC to DC.
6. Applications:
- Alternator: Alternators are widely used in automobiles to charge the battery and power electrical systems. They are also used in power generation stations to produce AC electricity.
- Generator: Generators are often found in smaller, portable applications, such as backup power sources, construction sites, and older electrical systems that require DC power.
7. Output Frequency:
- Alternator: Alternators produce AC with a specific frequency, usually 50 or 60 Hz, depending on the application and location.
- Generator: Generators do not have a fixed frequency; the output frequency depends on the rotational speed and design of the generator.
In summary, the primary difference between alternators and generators lies in the type of current they produce (AC vs. DC) and their operating principles. Alternators generate AC and are more efficient, while generators produce DC and may require more maintenance. The choice between them depends on the specific requirements of the application.
Read More
- Physical & chemical properties of water
- Difference Between Fuse And Circuit Breaker
- Difference Between Electromagnet And Permanent Magnet
- Blind Visually Impaired Optical Low Vision Aids
- Bar Magnet As An Equivalent Solenoid
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) Difference Between Alternator And Generator
1. What is the fundamental difference between an alternator and a generator?
The main difference lies in the type of current they produce. An alternator generates alternating current (AC), while a generator produces direct current (DC).
2. How do alternators and generators operate differently?
Alternators work on the principle of electromagnetic induction, producing AC through changing magnetic fields. Generators also use electromagnetic induction but typically employ a commutator to convert AC to DC.
3. Can you explain the output voltage differences between alternators and generators?
Alternators generally produce higher-voltage AC, while generators typically yield lower-voltage DC. Alternators may have built-in voltage regulation, making their output more stable.
4. Which one is easier to maintain, an alternator or a generator?
Alternators are generally easier to maintain because they have fewer moving parts and do not require components like brushes and commutators, which can wear out.
5. In terms of efficiency, which is better, an alternator or a generator?
Alternators are typically more efficient in converting mechanical energy into electrical energy compared to generators, which may have energy losses due to the commutator and AC-to-DC conversion.