Tag: isobaric isochoric isothermal and adiabatic processes
Difference Between Isothermal And Adiabatic Process
Difference Between Isothermal And Adiabatic Process: Certainly! Here’s a concise summary of the difference between isothermal and adiabatic processes:

Difference Between Isothermal And Adiabatic Process
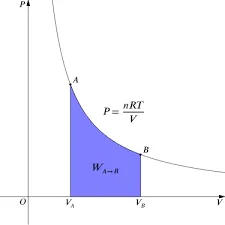
Isothermal Process:
- Temperature: Temperature remains constant throughout the process.
- Heat Transfer: Heat is exchanged with the surroundings to maintain temperature.
- Efficiency: Isothermal processes are more efficient due to constant temperature.
- Applications: Used in refrigeration and precise chemical reactions.
- Mathematical Representation: Follows the equation PV = constant for ideal gases.
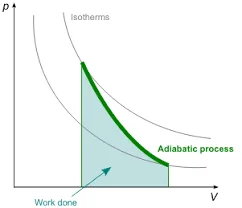
Adiabatic Process:
- Temperature: Temperature can change significantly during the process.
- Heat Transfer: No heat exchange with the surroundings; the process is thermally isolated.
- Efficiency: Adiabatic processes are generally less efficient due to temperature changes.
- Applications: Common in gas compression and expansion, like internal combustion engines.
- Mathematical Representation: Follows the equation PV^γ = constant, where γ is the ratio of specific heats.
In summary, the key distinction lies in temperature behavior and heat transfer. Isothermal processes maintain constant temperature with heat exchange, while adiabatic processes have temperature changes without heat exchange.
Read More
- Simple Harmonic Motion Examples
- Molecular Mass Of Calcium
- Molecular Weight of Chlorine
- Molecular Weight Of Benzene
- Lumen Meaning In Biology
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) Difference Between Isothermal And Adiabatic Process
1. What is an isothermal process?
An isothermal process is one in which the temperature of a system remains constant throughout the process. Heat is continuously added or removed to maintain this constant temperature.
2. What characterizes an adiabatic process?
An adiabatic process is defined by the absence of heat exchange with the surroundings. It occurs in thermally isolated systems where no heat is added to or removed from the system.
3. How does temperature change in an isothermal process?
In an isothermal process, the temperature remains constant, so there is no significant change in temperature.
4. Can you explain how temperature changes in an adiabatic process?
In an adiabatic process, temperature can change significantly. When work is done on or by the system, it can lead to temperature increases (compression) or decreases (expansion) without any heat exchange with the surroundings.
5. Which process is more efficient, isothermal or adiabatic?
Isothermal processes are generally more efficient because they maintain a constant temperature, allowing for maximum energy transfer. Adiabatic processes can be less efficient due to temperature changes.