Tag: national development class 10 notes
Class 10 Development Notes of NCERT Economics Chapter 1
Class 10 development notes: The CBSE Notes for Class 10 Economics Chapter 1 introduce the concept of ‘Development’ and serve as a foundational understanding for higher classes where more development issues are explored. In this chapter, students will find answers to critical questions about a country’s ideal state, essential requirements, prospects for a better life for all, coexistence principles, and possibilities for increased equality. These answers aren’t confined to Economics alone; They are also intertwined with insights from History and Political Science. Understanding development necessitates a holistic approach as our present way of life is profoundly shaped by our past.

Topics Covered in the Class 10 development Notes
- Overview
- What Development Promises —Different People, Different Goals.
- Income and Other Goals.
- National Development.
- How to Compare Different Countries or States?
- Income and Other Criteria.
- Public Facilities.
- Sustainability of Development.
What Development Promises —Different People, Different Goals
People are unique in their perspectives, values, and priorities, which lead them to pursue different paths and set distinct goals in life. What may be important and meaningful to one person might not hold the same significance for another.
This phrase emphasizes the diversity and individuality of human beings, acknowledging that each person has their own set of dreams, desires, and aims. It also highlights the need for understanding and respecting these differences, as it is natural for people to have diverse goals and aspirations based on their backgrounds, experiences, and personal preferences. Recognizing and embracing these distinctions is essential for building a harmonious and inclusive society.
Income and Other Goals

Individuals desire increased income, as it enables the acquisition of material possessions and services, influencing our lives significantly. Nevertheless, the quality of life is also influenced by non-material factors like equitable treatment, freedom, security, and respect for others. Development encompasses a combination of goals, wherein people seek not only better financial prospects but also other essential aspects of life. These developmental objectives extend beyond mere income enhancement, encompassing broader aspects that contribute to a fulfilling and meaningful existence.
Class 10 Development Notes
National Development
People can have different and even opposite ideas about how a country should progress and develop.
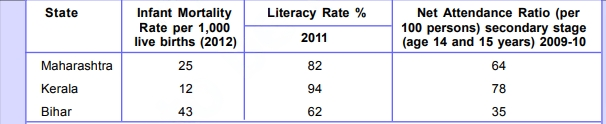
How to Compare Different Countries or States?
To compare countries, we often look at their income, which is a crucial factor in determining how developed they are. Countries with higher incomes are generally more developed than those with lower incomes. Instead of comparing total income, we consider the average income of each country to understand what an average person earns.
Average income is the total income of a country divided by its total population, known as per capital income.
Per Capita Income = Total Income of Country / Total Population of Country
In World Development Reports, per capita income is used to classify countries.
Countries with a per capita income of US$ 12,056 or more in 2017 are called rich countries. Low-income Countries has income of US$ 955 or less. For example, India falls into this category.
Income and Other Criteria
When we consider a country or an area, we must not only focus on the average income but also pay attention to public facilities, which are equally important.
Public Facilities: These are the services that the government offers to its people. Some essential public facilities include infrastructure, sanitation, public transport, healthcare, water supply, and more.
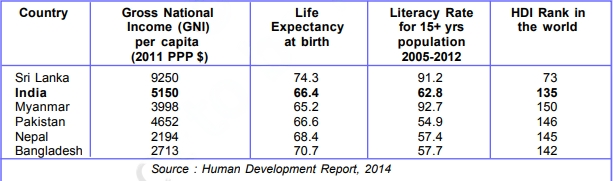
Sustainability of Development
Sustainable development means progress that fulfills the current needs without harming the ability of future generations to meet their needs. Scientists have been cautioning that our current type and level of development are not sustainable. Some examples of this unsustainability include the overuse of groundwater and the depletion of natural resources.
Summery of Class 10 Development Notes
The CBSE Notes for Class 10 Economics Chapter 1 introduce the concept of ‘Development,’ exploring critical questions about a country’s progress and goals.
It emphasizes the individuality of people, recognizing diverse aspirations and priorities. Development is not solely about income; non-material factors like freedom, security, and respect also influence the quality of life. The chapter explains how countries are compared using per capital income and considers public facilities’ importance.
It presents data comparing Maharashtra, Kerala, and Bihar. Moreover, we talk about the cool concept of sustainable development! It’s all about finding a way to fulfill our current needs without messing up the ability of future generations to meet their own needs. We also look at some not-so-cool examples of unsustainability, like overusing groundwater and depleting natural resources.
Frequently Asked Question – FAQs: Class 10 Development Notes
Q 1. Importance of “Development” chapter for students?
- The “Development” chapter introduces students to the multidimensional nature of development, beyond economic growth.
- It emphasizes that development should cater to diverse individual goals and aspirations.
- Students gain a holistic perspective on development, considering material and non-material factors.
- The chapter fosters critical thinking as students evaluate the meaning of development in the context of a country or region.
- They learn methods to compare and analyze development levels among different countries or states.
- The concept of sustainable development raises awareness about responsible resource use and environmental preservation.
- Students develop a sense of social responsibility and active citizenship, understanding development challenges in their communities and beyond.
- The chapter is relevant for those interested in economics, international relations, sociology, and environmental studies careers.
- It provides a global perspective, showcasing how different countries face distinct developmental challenges.
- Overall, the chapter equips students with knowledge and values essential for becoming informed and responsible global citizens.
Q 2. What are the various key factor to determine a country’s development?
- Key factors to determine a country’s development include GDP, GNI/GNP, and per capital income, reflecting economic prosperity and living standards.
- The Human Development Index (HDI) considers life expectancy, education, and income to assess human development levels.
- Education, literacy rate, and healthcare indicators provide insights into a nation’s human capital and well-being.
- Adequate infrastructure and public facilities, like transportation and access to basic services, are vital for economic and social development.
- Low unemployment rates and stable governance contribute to economic growth and societal stability.
- Income inequality and poverty rates reflect the distribution of wealth and opportunities within a country.
- Environmental sustainability and commitment to conservation impact a country’s long-term development.
- Access to clean water and sanitation facilities is essential for public health and human development.
- Gender equality and empowering women contribute to social progress and inclusive development.
- These factors collectively offer a comprehensive assessment of a country’s development status, guiding policymakers in prioritizing development strategies.
Q 3. When a country will known as “Developed Country”?
A “Developed Country” refers to a nation that has achieved a high level of economic prosperity, industrialization, technology, and social well-being.
The categorization varies among different organizations and indices. Common features of developed countries include high GDP per capita, advanced infrastructure, low poverty, access to quality healthcare and education, low infant mortality, high life expectancy, strong governance, and a high standard of living.
Examples of developed countries include the United States, Canada, Germany, Japan, Australia, and several European nations. Development is an ongoing process, and countries may transition from developing to developed status based on socio-economic improvements over time.